Triplex-forming oligonucleotides targeting c-MYC potentiate the anti-tumor activity of gemcitabine in a mouse model of human cancer
- PMID: 23681918
- PMCID: PMC4004705
- DOI: 10.1002/mc.22026
Triplex-forming oligonucleotides targeting c-MYC potentiate the anti-tumor activity of gemcitabine in a mouse model of human cancer
Abstract
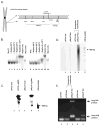
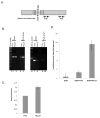
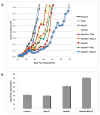
Antimetabolite chemotherapy remains an essential cancer treatment modality, but often produces only marginal benefit due to the lack of tumor specificity, the development of drug resistance, and the refractoriness of slowly proliferating cells in solid tumors. Here, we report a novel strategy to circumvent the proliferation-dependence of traditional antimetabolite-based therapies. Triplex-forming oligonucleotides (TFOs) were used to target site-specific DNA damage to the human c-MYC oncogene, thereby inducing replication-independent, unscheduled DNA repair synthesis (UDS) preferentially in the TFO-targeted region. The TFO-directed UDS facilitated incorporation of the antimetabolite, gemcitabine (GEM), into the damaged oncogene, thereby potentiating the anti-tumor activity of GEM. Mice bearing COLO 320DM human colon cancer xenografts (containing amplified c-MYC) were treated with a TFO targeted to c-MYC in combination with GEM. Tumor growth inhibition produced by the combination was significantly greater than with either TFO or GEM alone. Specific TFO binding to the genomic c-MYC gene was demonstrated, and TFO-induced DNA damage was confirmed by NBS1 accumulation, supporting a mechanism of enhanced efficacy of GEM via TFO-targeted DNA damage-induced UDS. Thus, coupling antimetabolite chemotherapeutics with a strategy that facilitates selective targeting of cells containing amplification of cancer-relevant genes can improve their activity against solid tumors, while possibly minimizing host toxicity.
Keywords: DNA-reactive agents; combination chemotherapy; oncogenes; triplex-forming oligonucleotides; xenograft models.
© 2013 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors disclose no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts and Figures 2010. 2010.
-
- Rockwell S, Grindey GB. Effect of 2',2'-difluorodeoxycytidine on the viability and radiosensitivity of EMT6 cells in vitro. Oncol Res. 1992;4(4–5):151–155. - PubMed
-
- Huang P, Plunkett W. Fludarabine- and gemcitabine-induced apoptosis: incorporation of analogs into DNA is a critical event. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1995;36(3):181–188. - PubMed
-
- Baselga J, Tripathy D, Mendelsohn J, et al. Phase II study of weekly intravenous trastuzumab (Herceptin) in patients with HER2/neu-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer. Semin Oncol. 1999;26(4 Suppl 12):78–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

