Analytical Ultracentrifugation as a Tool for Studying Protein Interactions
- PMID: 23682298
- PMCID: PMC3652485
- DOI: 10.1007/s12551-013-0106-2
Analytical Ultracentrifugation as a Tool for Studying Protein Interactions
Abstract
The last two decades have led to significant progress in the field of analytical ultracentrifugation driven by instrumental, theoretical, and computational methods. This review will highlight key developments in sedimentation equilibrium (SE) and sedimentation velocity (SV) analysis. For SE, this includes the analysis of tracer sedimentation equilibrium at high concentrations with strong thermodynamic non-ideality, and for ideally interacting systems the development of strategies for the analysis of heterogeneous interactions towards global multi-signal and multi-speed SE analysis with implicit mass conservation. For SV, this includes the development and applications of numerical solutions of the Lamm equation, noise decomposition techniques enabling direct boundary fitting, diffusion deconvoluted sedimentation coefficient distributions, and multi-signal sedimentation coefficient distributions. Recently, effective particle theory has uncovered simple physical rules for the co-migration of rapidly exchanging systems of interacting components in SV. This has opened new possibilities for the robust interpretation of the boundary patterns of heterogeneous interacting systems. Together, these SE and SV techniques have led to new approaches to study macromolecular interactions across the entire the spectrum of affinities, including both attractive and repulsive interactions, in both dilute and highly concentrated solutions, which can be applied to single-component solutions of self-associating proteins as well as the study of multi-protein complex formation in multi-component solutions.
Keywords: effective particle theory; global analysis; multi-protein complexes; multi-signal analysis; sedimentation equilibrium; sedimentation velocity.
Figures
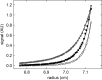
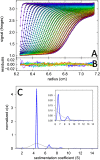
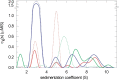
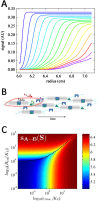
References
-
- Balbo A, Brown P, Braswell E, Schuck P. Measuring protein-protein interactions by equilibrium sedimentation. Curr Protoc Immunol. 2007;18:18.8. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

