Statistically enhanced spectral counting approach to TCDD cardiac toxicity in the adult zebrafish heart
- PMID: 23682714
- PMCID: PMC3740750
- DOI: 10.1021/pr400312u
Statistically enhanced spectral counting approach to TCDD cardiac toxicity in the adult zebrafish heart
Abstract
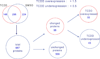
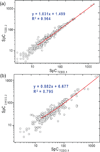
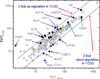
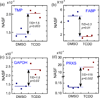
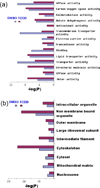
2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) is a persistent environmental pollutant and teratogen that produces cardiac toxicity in the developing zebrafish. Here we adopted a label free quantitative proteomic approach based on normalized spectral abundance factor (NSAF) to investigate the disturbance of the cardiac proteome induced by TCDD in the adult zebrafish heart. The protein expression level changes between heart samples from TCDD-treated and control zebrafish were systematically evaluated by a large scale MudPIT analysis, which incorporated triplicate analyses for both control and TCDD-exposed heart proteomic samples to overcome the data-dependent variation in shotgun proteomic experiments and obtain a statistically significant protein data set with improved quantification confidence. A total of 519 and 443 proteins were identified in hearts collected from control and TCDD-treated zebrafish, respectively, among which 106 proteins showed statistically significant expression changes. After correcting for the experimental variation between replicate analyses by statistical evaluation, 55 proteins exhibited NSAF ratios above 2 and 43 proteins displayed NSAF ratios smaller than 0.5, with statistical significance by t test (p < 0.05). The proteins identified as altered by TCDD encompass a wide range of biological functions including calcium handling, myocardium cell architecture, energy production and metabolism, mitochondrial homeostasis, and stress response. Collectively, our results indicate that TCDD exposure alters the adult zebrafish heart in a way that could result in cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure and suggests a potential mechanism for the diastolic dysfunction observed in TCDD-exposed embryos.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Heart malformation is an early response to TCDD in embryonic zebrafish.Toxicol Sci. 2005 Apr;84(2):368-77. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfi073. Epub 2005 Jan 5. Toxicol Sci. 2005. PMID: 15635151
-
Cardiac toxicity by sublethal 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin correlates with its anti-proliferation effect on cardiomyocytes in zebrafish embryos.Environ Toxicol Chem. 2015 Feb;34(2):420-8. doi: 10.1002/etc.2822. Epub 2015 Jan 6. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25477153
-
Cardiovascular gene expression profiles of dioxin exposure in zebrafish embryos.Toxicol Sci. 2005 May;85(1):683-93. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfi116. Epub 2005 Feb 16. Toxicol Sci. 2005. PMID: 15716485
-
Understanding dioxin developmental toxicity using the zebrafish model.Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol. 2006 Jan;76(1):7-18. doi: 10.1002/bdra.20216. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol. 2006. PMID: 16333842 Review.
-
Mechanisms of Developmental Toxicity of Dioxins and Related Compounds.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jan 31;20(3):617. doi: 10.3390/ijms20030617. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30708991 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Expression and Characterization of Human Fragile X Mental Retardation Protein Isoforms and Interacting Proteins in Human Cells.Proteomics Insights. 2019 Mar 3;10:1178641818825268. doi: 10.1177/1178641818825268. eCollection 2019. Proteomics Insights. 2019. PMID: 30853789 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of differentially expressed serum proteins in infectious purpura fulminans.Dis Markers. 2014;2014:698383. doi: 10.1155/2014/698383. Epub 2014 Feb 10. Dis Markers. 2014. PMID: 24659849 Free PMC article.
-
Studying the Impact of Persistent Organic Pollutants Exposure on Human Health by Proteomic Analysis: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 17;23(22):14271. doi: 10.3390/ijms232214271. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430748 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Quantitative Phosphoproteomics and Cell-based Functional Screening Reveals Specific Pathological Cardiac Hypertrophy-related Phosphorylation Sites.Mol Cells. 2021 Jul 31;44(7):500-516. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2021.4002. Mol Cells. 2021. PMID: 34158421 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kociba RJ, Schwetz BA. Toxicity of 2, 3, 7, 8-tetrachlorodibenzo-para-dioxin (TCDD) Drug Metabolism Reviews. 1982;13(3):387–406. - PubMed
-
- Lilienfeld DE, Gallo MA. 2,4-D, 2,4,5-T, and 2,3,7,8-TCDD - An Overview. Epidemiologic Reviews. 1989;11:28–58. - PubMed
-
- Skene SA, Dewhurst IC, Greenberg M. Polychlorinated dibenzo-para-dioxins and polychlorinated dibenzofurans - the risks to human health - a review. Human Toxicology. 1989;8(3):173–203. - PubMed
-
- McNulty WP. Fetotoxicity of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-para-dioxin (TCDD) for Rhesus Macaques (Macaca-mulatta) American Journal of Primatology. 1984;6(1):41–47. - PubMed
-
- Hassoun EA, Walter AC, Alsharif NZ, Stohs SJ. Modulation of TCDD-induced fetotoxicity and oxidative stress in embryonic and placental tissues of C57BL/6J mice by vitamin E succinate and ellagic acid. Toxicology. 1997;124(1):27–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

