Chemopreventive and anti-cancer efficacy of silibinin against growth and progression of lung cancer
- PMID: 23682778
- PMCID: PMC3924887
- DOI: 10.1080/01635581.2013.785004
Chemopreventive and anti-cancer efficacy of silibinin against growth and progression of lung cancer
Abstract
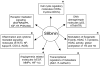
The use of systemic chemotherapeutic drugs and molecular-targeted therapies in the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic lung cancer has its limitations due to the associated acute and cumulative dose limiting toxicities and acquisition of drug resistance. Prevention and therapeutic intervention by dietary agents including nutraceuticals which are non-toxic, cost-effective, and physiologically bioavailable, are emerging approaches in lung cancer management. In this regard, silibinin, a natural flavonolignan, has been rigorously evaluated for the prevention and growth control of lung cancer through extensive in vitro and in vivo studies. Successful studies conducted so far, have established that silibinin is effective both alone and in combination with other agents (e.g., chemotherapeutic and epigenetic agents) in significantly inhibiting the growth of lung cancer cells. In vivo, its effects have been shown to be mediated through inhibition of proliferation, angiogenesis and epigenetic-related events. Therefore, the present review focuses on encompassing the efficacy and mechanisms of silibinin against lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Stem cell-like ALDH(bright) cellular states in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer: a novel mechanism of acquired resistance to erlotinib targetable with the natural polyphenol silibinin.Cell Cycle. 2013 Nov 1;12(21):3390-404. doi: 10.4161/cc.26417. Epub 2013 Sep 17. Cell Cycle. 2013. PMID: 24047698 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic modifications and p21-cyclin B1 nexus in anticancer effect of histone deacetylase inhibitors in combination with silibinin on non-small cell lung cancer cells.Epigenetics. 2012 Oct;7(10):1161-72. doi: 10.4161/epi.22070. Epub 2012 Sep 10. Epigenetics. 2012. PMID: 22965008 Free PMC article.
-
Oral silibinin inhibits lung tumor growth in athymic nude mice and forms a novel chemocombination with doxorubicin targeting nuclear factor kappaB-mediated inducible chemoresistance.Clin Cancer Res. 2004 Dec 15;10(24):8641-7. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-1435. Clin Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15623648
-
Prostate cancer prevention by silibinin.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2004 Feb;4(1):1-11. doi: 10.2174/1568009043481605. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2004. PMID: 14965263 Review.
-
Combinatorial strategies for cancer eradication by silibinin and cytotoxic agents: efficacy and mechanisms.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2007 Sep;28(9):1466-75. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7254.2007.00691.x. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2007. PMID: 17723180 Review.
Cited by
-
Use of gold nanoparticle-silibinin conjugates: A novel approach against lung cancer cells.Front Chem. 2022 Oct 13;10:1018759. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2022.1018759. eCollection 2022. Front Chem. 2022. PMID: 36311430 Free PMC article.
-
Genkwanin nanosuspensions: a novel and potential antitumor drug in breast carcinoma therapy.Drug Deliv. 2017 Nov;24(1):1491-1500. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2017.1384519. Drug Deliv. 2017. PMID: 28961040 Free PMC article.
-
Stem cell-like ALDH(bright) cellular states in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer: a novel mechanism of acquired resistance to erlotinib targetable with the natural polyphenol silibinin.Cell Cycle. 2013 Nov 1;12(21):3390-404. doi: 10.4161/cc.26417. Epub 2013 Sep 17. Cell Cycle. 2013. PMID: 24047698 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy induction by silibinin positively contributes to its anti-metastatic capacity via AMPK/mTOR pathway in renal cell carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Apr 15;16(4):8415-29. doi: 10.3390/ijms16048415. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25884331 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-Activity Relationship of Hydroxycinnamic Acid Derivatives for Cooperating with Carnosic Acid and Calcitriol in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells.Biomedicines. 2021 Oct 21;9(11):1517. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9111517. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34829746 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amercian Cancer Society. Cancer Facts and Figures. 2012
-
- Denlinger CE, Ikonomidis JS, Reed CE, Spinale FG. Epithelial to mesenchymal transition: the doorway to metastasis in human lung cancers. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2010;140:505–513. - PubMed
-
- Travis WD. Classification of lung cancer. Semin Roentgenol. 2011;46:178–186. - PubMed
-
- Schiller JH. Current standards of care in small-cell and non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncology. 2001;61 (Suppl 1):3–13. - PubMed
-
- Collins LG, Haines C, Perkel R, Enck RE. Lung cancer: diagnosis and management. Am Fam Physician. 2007;75:56–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
