Assessment of insulin action on carbohydrate metabolism: physiological and non-physiological methods
- PMID: 23683103
- PMCID: PMC3662485
- DOI: 10.1111/dme.12189
Assessment of insulin action on carbohydrate metabolism: physiological and non-physiological methods
Abstract
Carbohydrate metabolism in humans is regulated by insulin secretion from pancreatic β-cells and glucose disposal by insulin-sensitive tissues. Insulin facilitates glucose utilization in peripheral tissues and suppresses hepatic glucose production. Any defects in insulin action predispose an individual to glucose intolerance and Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Early detection of defects in insulin action could provide opportunities to prevent or delay progression of the disease state. There are different approaches to assess insulin action. Initial methods, such as peripheral insulin concentration and simple indices, have several limitations. Subsequently, researchers developed methodologies using intravenous glucose infusion to determine glucose fluxes. However, these methodologies are limited by being non-physiological. Newer, innovative techniques that have been developed are more sophisticated and physiological. By modelling glucose kinetics using isotope dilution techniques, several robust parameters can be obtained that are physiologically relevant and sound. This brief review summarizes most of the non-physiological and physiological methodologies used to measure the variables of insulin action.
© 2013 The Authors. Diabetic Medicine © 2013 Diabetes UK.
Figures
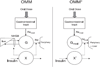

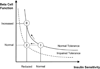
Similar articles
-
Shift to Fatty Substrate Utilization in Response to Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibition in Subjects Without Diabetes and Patients With Type 2 Diabetes.Diabetes. 2016 May;65(5):1190-5. doi: 10.2337/db15-1356. Epub 2016 Feb 9. Diabetes. 2016. PMID: 26861783 Clinical Trial.
-
A model of type 2 diabetes in the guinea pig using sequential diet-induced glucose intolerance and streptozotocin treatment.Dis Model Mech. 2017 Feb 1;10(2):151-162. doi: 10.1242/dmm.025593. Epub 2017 Jan 12. Dis Model Mech. 2017. PMID: 28093504 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of defects in glucose uptake to carbohydrate intolerance in liver cirrhosis: assessment during physiological glucose and insulin concentrations.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2005 Jun;288(6):G1135-43. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00278.2004. Epub 2005 Jan 6. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15637182
-
THE PHYSIOLOGY BEHIND DIABETES MELLITUS IN PATIENTS WITH PHEOCHROMOCYTOMA: A REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE.Endocr Pract. 2017 Aug;23(8):999-1005. doi: 10.4158/EP171914.RA. Epub 2017 Jun 14. Endocr Pract. 2017. PMID: 28613940 Review.
-
Glucocorticoids and beta-cell function.Endokrynol Pol. 2017;68(5):568-573. doi: 10.5603/EP.2017.0060. Endokrynol Pol. 2017. PMID: 29168546 Review.
Cited by
-
The Burden of Carbohydrates in Health and Disease.Nutrients. 2022 Sep 15;14(18):3809. doi: 10.3390/nu14183809. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36145184 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biometric Strategies to Improve Vaccine Immunogenicity and Effectiveness.Biomimetics (Basel). 2025 Jul 3;10(7):439. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics10070439. Biomimetics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40710252 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pancreas-enriched miRNAs are altered in the circulation of subjects with diabetes: a pilot cross-sectional study.Sci Rep. 2016 Aug 25;6:31479. doi: 10.1038/srep31479. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27558530 Free PMC article.
-
The control of hyperglycemia by a novel trypsin resistant oral insulin preparation in alloxan induced type I diabetic mice.Sci Rep. 2016 May 26;6:26789. doi: 10.1038/srep26789. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27226415 Free PMC article.
-
Role of insulin and insulin resistance in androgen excess disorders.World J Diabetes. 2021 May 15;12(5):616-629. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i5.616. World J Diabetes. 2021. PMID: 33995849 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hollenbeck CB, Chen N, Chen Y-DI, Reaven GM. Relationship between the plasma insulin response to oral glucose and insulin-stimulated glucose utilization in normal subjects. Diabetes. 1984;33:460–463. - PubMed
-
- Olefsky JM, Farquhar JW, Reaven GM. Relationship between fasting plasma insulin level and resistance to insulin-mediated glucose uptake in normal and diabetic subjects. Diabetes. 1973;22:507–513. - PubMed
-
- Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and β-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia. 1985;28:412–419. - PubMed
-
- Basu R, Dalla Man C, Campioni M, Basu A, Klee G, Toffolo G, et al. Effects of age and sex on postprandial glucose metabolism: differences in glucose turnover, insulin secretion, insulin action, and hepatic insulin extraction. Diabetes. 2006;55:2001–2014. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

