Activation of p53 with Nutlin-3a radiosensitizes lung cancer cells via enhancing radiation-induced premature senescence
- PMID: 23683497
- PMCID: PMC3739976
- DOI: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2013.04.017
Activation of p53 with Nutlin-3a radiosensitizes lung cancer cells via enhancing radiation-induced premature senescence
Abstract
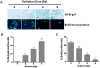
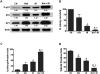
Radiotherapy is routinely used for the treatment of lung cancer. However, the mechanisms underlying ionizing radiation (IR)-induced senescence and its role in lung cancer treatment are poorly understood. Here, we show that IR suppresses the proliferation of human non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells via an apoptosis-independent mechanism. Further investigations reveal that the anticancer effect of irradiation correlates well with IR-induced premature senescence, as evidenced by increased senescence-associated β-glactosidase (SA-β-gal) staining, decreased BrdU incorporation and elevated expression of p16(INK4a) (p16) in irradiated NSCLC cells. Mechanistic studies indicate that the induction of senescence is associated with activation of the p53-p21 pathway, and that inhibition of p53 transcriptional activity by PFT-α attenuates IR-induced tumor cell killing and senescence. Gain-of-function assays demonstrate that restoration of p53 expression sensitizes H1299 cells to irradiation, whereas knockdown of p53 expression by siRNA inhibits IR-induced senescence in H460 cells. Furthermore, treatment with Nutlin-3a, a small molecule inhibitor of MDM2, enhances IR-induced tumor cell killing and senescence by stabilizing the activation of the p53-p21 signaling pathway. Taken together, these findings demonstrate for the first time that pharmacological activation of p53 by Nutlin-3a can sensitize lung cancer cells to radiation therapy via promoting IR-induced premature senescence.
Keywords: Non-small cell lung cancer; Nutilin-3a; Radiotherapy; Senescence; p53; siRNA.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Elmore LW, Rehder CW, Di X, McChesney PA, Jackson-Cook CK, et al. Adriamycin-induced senescence in breast tumor cells involves functional p53 and telomere dysfunction. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:35509–15. - PubMed
-
- te Poele RH, Okorokov AL, Jardine L, Cummings J, Joel SP. DNA damage is able to induce senescence in tumor cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res. 2002;62:1876–83. - PubMed
-
- Rebbaa A, Zheng X, Chou PM, Mirkin BL. Caspase inhibition switches doxorubicin-induced apoptosis to senescence. Oncogene. 2003;22:2805–11. - PubMed
-
- Yin DX, Schimke RT. BCL-2 expression delays drug-induced apoptosis but does not increase clonogenic survival after drug treatment in HeLa cells. Cancer Res. 1995;55:4922–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

