Molecular mechanisms of antiseizure drug activity at GABAA receptors
- PMID: 23683707
- PMCID: PMC3766376
- DOI: 10.1016/j.seizure.2013.04.015
Molecular mechanisms of antiseizure drug activity at GABAA receptors
Abstract
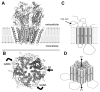
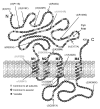
The GABAA receptor (GABAAR) is a major target of antiseizure drugs (ASDs). A variety of agents that act at GABAARs s are used to terminate or prevent seizures. Many act at distinct receptor sites determined by the subunit composition of the holoreceptor. For the benzodiazepines, barbiturates, and loreclezole, actions at the GABAAR are the primary or only known mechanism of antiseizure action. For topiramate, felbamate, retigabine, losigamone and stiripentol, GABAAR modulation is one of several possible antiseizure mechanisms. Allopregnanolone, a progesterone metabolite that enhances GABAAR function, led to the development of ganaxolone. Other agents modulate GABAergic "tone" by regulating the synthesis, transport or breakdown of GABA. GABAAR efficacy is also affected by the transmembrane chloride gradient, which changes during development and in chronic epilepsy. This may provide an additional target for "GABAergic" ASDs. GABAAR subunit changes occur both acutely during status epilepticus and in chronic epilepsy, which alter both intrinsic GABAAR function and the response to GABAAR-acting ASDs. Manipulation of subunit expression patterns or novel ASDs targeting the altered receptors may provide a novel approach for seizure prevention.
Keywords: Antiepileptic drugs; Chloride channel; Epilepsy; GABA receptor; Inhibition; Seizures.
Copyright © 2013 British Epilepsy Association. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Treiman DM. GABAergic mechanisms in epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2001;42(Suppl 3):8–12. - PubMed
-
- Olsen RW, DeLorey TM, Gordey M, Kang MH. GABA receptor function and epilepsy. Advances in Neurology. 1999;79:499–510. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Ari Y. Seizures beget seizures: the quest for GABA as a key player. Crit Rev.Neurobiol. 2006;18:135–144. - PubMed
-
- Sperk G, Furtinger S, Schwarzer C, Pirker S. GABA and its receptors in epilepsy. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. 2004;548:92–103. - PubMed
-
- Macdonald RL, Olsen RW. GABAA receptor channels. Annual Reviews of Neuroscience. 1994;17:569–602. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

