Roles of virulence genes (PsaA and CpsA) on the invasion of Streptococcus pneumoniae into blood system
- PMID: 23683724
- PMCID: PMC3695859
- DOI: 10.1186/2047-783X-18-14
Roles of virulence genes (PsaA and CpsA) on the invasion of Streptococcus pneumoniae into blood system
Abstract
Background: Streptococcus pneumoniae (SP) is the major cause of childhood mortality worldwide, we need to understand virulence genes of SP so can better target the treatment.We investigated the expression of virulence genes PsaA and CpsA in different strains of SP interacting with monocyte cell line (THP-1) or pneumocyte cell line (A549) and the possible mechanism of SP invasion of the blood system.
Methods: A total of 23 strains of SP were collected from hospitalized patients (blood-derived and sputum-derived) in the Second Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical College. The strains and ATCC 49619 were cultured, and RNAs were extracted. THP-1 and A549 cells were stimulated by different SP and ATCC 49619 for 4 h and 8 h, respectively. Quantitative real-time PCR was used to analyze the mRNA expression of PsaA and CpsA. The data were analyzed by SPSS 17.0.
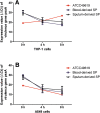
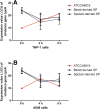
Results: The mRNA level of PsaA and CpsA were all significantly increased in clinical SP strains when compared to ATCC49619 after tedTHP-1 and A549 cells were stimulated. Clinical SPs showed higher virulence compared with ATCC49619.
Conclusions: The expression of CpsA is the basis of the pathogenicity of SP. The expression of virulence gene PsaA may be helpful to the invasion of SP to the blood system.
Figures

Similar articles
-
In vitro expression of Streptococcus pneumoniae ply gene in human monocytes and pneumocytes.Eur J Med Res. 2015 May 7;20(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s40001-015-0142-4. Eur J Med Res. 2015. PMID: 25943628 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of clinical isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae on THP-1 human monocytic cells.Mol Med Rep. 2013 Nov;8(5):1570-4. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2013.1688. Epub 2013 Sep 17. Mol Med Rep. 2013. PMID: 24045590
-
Sequence heterogeneity of PsaA, a 37-kilodalton putative adhesin essential for virulence of Streptococcus pneumoniae.Infect Immun. 1996 Dec;64(12):5255-62. doi: 10.1128/iai.64.12.5255-5262.1996. Infect Immun. 1996. PMID: 8945574 Free PMC article.
-
Pneumococcal surface adhesin A (PsaA): a review.Crit Rev Microbiol. 2008;34(3-4):131-42. doi: 10.1080/10408410802275352. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18728990 Review.
-
Gene elements that regulate Streptococcus pneumoniae virulence and immunity evasion.Curr Gene Ther. 2013 Feb;13(1):51-64. doi: 10.2174/156652313804806615. Curr Gene Ther. 2013. PMID: 23189947 Review.
Cited by
-
In vitro expression of Streptococcus pneumoniae ply gene in human monocytes and pneumocytes.Eur J Med Res. 2015 May 7;20(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s40001-015-0142-4. Eur J Med Res. 2015. PMID: 25943628 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification of genes essential for the survival of Streptococcus pneumoniae in human saliva.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 25;9(2):e89541. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089541. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24586856 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying genes associated with invasive disease in S. pneumoniae by applying a machine learning approach to whole genome sequence typing data.Sci Rep. 2019 Mar 11;9(1):4049. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-40346-7. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30858412 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of different Streptococcus pneumoniae on the secretion of interleukin and adhesin from THP-1 monocytes.J Clin Lab Anal. 2019 Sep;33(7):e22927. doi: 10.1002/jcla.22927. Epub 2019 Jun 23. J Clin Lab Anal. 2019. PMID: 31231868 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization, antibiotic resistance pattern and capsular types of invasive Streptococcus pneumoniae isolated from clinical samples in Tehran, Iran.BMC Microbiol. 2020 Jun 16;20(1):167. doi: 10.1186/s12866-020-01855-y. BMC Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32546124 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

