Improving epidemiologic data analyses through multivariate regression modelling
- PMID: 23683753
- PMCID: PMC3691873
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-7622-10-4
Improving epidemiologic data analyses through multivariate regression modelling
Abstract
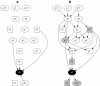
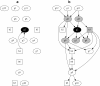
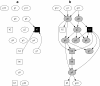
: Regression modelling is one of the most widely utilized approaches in epidemiological analyses. It provides a method of identifying statistical associations, from which potential causal associations relevant to disease control may then be investigated. Multivariable regression - a single dependent variable (outcome, usually disease) with multiple independent variables (predictors) - has long been the standard model. Generalizing multivariable regression to multivariate regression - all variables potentially statistically dependent - offers a far richer modelling framework. Through a series of simple illustrative examples we compare and contrast these approaches. The technical methodology used to implement multivariate regression is well established - Bayesian network structure discovery - and while a relative newcomer to the epidemiological literature has a long history in computing science. Applications of multivariate analysis in epidemiological studies can provide a greater understanding of disease processes at the population level, leading to the design of better disease control and prevention programs.
Figures
References
-
- Buntine W. Proceedings of Seventh Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence. Los Angeles: Morgan Kaufmann; 1991. Theory refinement on Bayesian networks; pp. 52–60.
-
- Heckerman D, Geiger D, Chickering DM. Learning Bayesian networks - The combination of knowledge and statistical-data. Mach Learn. 1995;20(3):197–243.
-
- Jensen FV. Bayesian Network and Decision Graphs. New York: Springer-Verlag; 2001.
-
- Lauritzen SL. Graphical Models. Oxford: Univ Press; 1996.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

