Functional analysis of the stem loop S3 and S4 structures in the coronavirus 3'UTR
- PMID: 23683838
- PMCID: PMC3700632
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2013.04.021
Functional analysis of the stem loop S3 and S4 structures in the coronavirus 3'UTR
Abstract
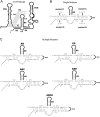
We designed a series of mutations to separately destabilize two helical stems (designated S3 and S4) predicted by a covariation-based model of the coronavirus 3'UTR (Zust et al., 2008). Mouse hepatitis virus genomes containing three or four nucleotide mutations that destabilize either S3 or S4 were viable, whereas genomes carrying these mutations in both S3 and S4 were not viable. A genome carrying these mutations in S3 and S4 plus compensatory mutations restoring base-pairing yielded a virus with wild type phenotype. Larger mutations which completely disrupt S3 or S4 generated various phenotypes. Mutations opening up S3 were lethal. Disruptions of S4 generated both viable and lethal mutants. Genomes carrying the original mutations in S3 or S4 plus compensatory mutations restoring base pairing were viable and had robust growth phenotypes. These results support the Zust model for the coronavirus 3'UTR and suggest that the S3 stem is required for virus viability.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The structure and functions of coronavirus genomic 3' and 5' ends.Virus Res. 2015 Aug 3;206:120-33. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2015.02.025. Epub 2015 Feb 28. Virus Res. 2015. PMID: 25736566 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mouse hepatitis virus stem-loop 4 functions as a spacer element required to drive subgenomic RNA synthesis.J Virol. 2011 Sep;85(17):9199-209. doi: 10.1128/JVI.05092-11. Epub 2011 Jun 29. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21715502 Free PMC article.
-
Structural lability in stem-loop 1 drives a 5' UTR-3' UTR interaction in coronavirus replication.J Mol Biol. 2008 Mar 28;377(3):790-803. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.01.068. Epub 2008 Feb 2. J Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18289557 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of an essential RNA secondary structure in the 3' untranslated region of the murine coronavirus genome.J Virol. 2000 Aug;74(15):6911-21. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.15.6911-6921.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10888630 Free PMC article.
-
3'UTRs of carmoviruses.Virus Res. 2015 Aug 3;206:27-36. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2015.01.023. Epub 2015 Feb 4. Virus Res. 2015. PMID: 25662021 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 by Targeting Conserved Viral RNA Structures and Sequences.Front Chem. 2021 Dec 23;9:802766. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2021.802766. eCollection 2021. Front Chem. 2021. PMID: 35004621 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of the Role of Hexamer AGUAAA and Poly(A) Tail in Coronavirus Polyadenylation.PLoS One. 2016 Oct 19;11(10):e0165077. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0165077. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27760233 Free PMC article.
-
Emergency Services of Viral RNAs: Repair and Remodeling.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2018 Mar 14;82(2):e00067-17. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00067-17. Print 2018 Jun. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2018. PMID: 29540453 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Short- and Long-Range RNA-RNA Interactome of SARS-CoV-2.Mol Cell. 2020 Dec 17;80(6):1067-1077.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.11.004. Epub 2020 Nov 5. Mol Cell. 2020. PMID: 33259809 Free PMC article.
-
The structure and functions of coronavirus genomic 3' and 5' ends.Virus Res. 2015 Aug 3;206:120-33. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2015.02.025. Epub 2015 Feb 28. Virus Res. 2015. PMID: 25736566 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Boursnell M.E.G., Binss M.M., Foulds I.J., Brown T.K.K. Sequences of the nucleocapsid genes from two strains of avian infectious bronchitis virus. J. Gen. Virol. 1985;66:573–580. - PubMed
-
- Britton P.a.D.C. Nidovirus genome organization and expression mechanism. In: Perlman S., Gallagher T., Snijder E.J., editors. Nidoviruses. ASM Press; Washington D.C: 2008. pp. 29–46.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

