The WU-Minn Human Connectome Project: an overview
- PMID: 23684880
- PMCID: PMC3724347
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.05.041
The WU-Minn Human Connectome Project: an overview
Abstract
The Human Connectome Project consortium led by Washington University, University of Minnesota, and Oxford University is undertaking a systematic effort to map macroscopic human brain circuits and their relationship to behavior in a large population of healthy adults. This overview article focuses on progress made during the first half of the 5-year project in refining the methods for data acquisition and analysis. Preliminary analyses based on a finalized set of acquisition and preprocessing protocols demonstrate the exceptionally high quality of the data from each modality. The first quarterly release of imaging and behavioral data via the ConnectomeDB database demonstrates the commitment to making HCP datasets freely accessible. Altogether, the progress to date provides grounds for optimism that the HCP datasets and associated methods and software will become increasingly valuable resources for characterizing human brain connectivity and function, their relationship to behavior, and their heritability and genetic underpinnings.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

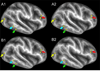
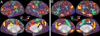
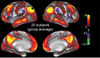
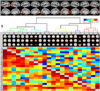
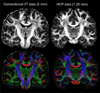
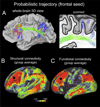

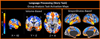
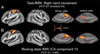
References
-
- Andersson JLR, Xu J, Yacoub E, Auerbach E, Moeller S, Ugurbil K. A comprehensive Gaussian process framework for correcting distortions and movements in diffusion images. Melbourne, Australia: INSERM Annual Meeting; May, 2012.
-
- Azevedo FA, Carvalho LR, Grinberg LT, Farfel JM, Ferretti RE, Leite RE, Jacob Filho W, Lent R, Herculano-Houzel S. Equal numbers of neuronal and nonneuronal cells make the human brain an isometrically scaled-up primate brain. The Journal of comparative neurology. 2009;513:532–541. - PubMed
-
- Beckmann CF, Smith SM. Probabilistic independent component analysis for functional magnetic resonance imaging. IEEE transactions on medical imaging. 2004;23:137–152. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

