A comparison of the efficiency of five different commercial DNA extraction kits for extraction of DNA from faecal samples
- PMID: 23684993
- PMCID: PMC5809576
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mimet.2013.05.008
A comparison of the efficiency of five different commercial DNA extraction kits for extraction of DNA from faecal samples
Abstract
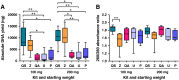
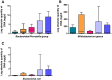
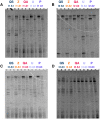
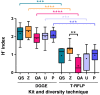
Differences in the composition of the gut microbiota have been associated with a range of diseases using culture-independent methods. Reliable extraction of nucleic acid is a key step in identifying the composition of the faecal microbiota. Five widely used commercial deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) extraction kits (QIAsymphony® Virus/Bacteria Midi Kit (kit QS), ZR Fecal DNA MiniPrep™ (kit Z), QIAamp® DNA Stool Mini Kit (kit QA), Ultraclean® Fecal DNA Isolation Kit (kit U) and PowerSoil® DNA Isolation Kit (kit P)) were evaluated, using human faecal samples. Yield, purity and integrity of total genomic DNA were compared spectrophotometrically and using gel electrophoresis. Three bacteria, commonly found in human faeces were quantified using real time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) and total bacterial diversity was studied using denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) as well as terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism (T-RFLP). The measurements of DNA yield and purity exhibited variations between the five kits tested in this study. Automated kit QS exhibited the best quality and highest quantity of DNA. All kits were shown to be reproducible with CV values≤0.46 for DNA extraction. qPCR results showed that all kits were uniformly efficient for extracting DNA from the selected target bacteria. DGGE and T-RFLP produced the highest diversity scores for DNA extracted using kit Z (H'=2.30 and 1.27) and kit QS (H'=2.16 and 0.94), which also extracted the highest DNA yields compared to the other kits assessed.
Keywords: Bacteria; DGGE; DNA extraction; Faeces; Real-time PCR; T-RFLP.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Bahl M.I., Bergström A., Licht T.R. Freezing fecal samples prior to DNA extraction affects the Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes ratio determined by downstream quantitative PCR analysis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2012;329(2):193–197. - PubMed
-
- Dave M., Higgins P.D., Middha S., Rioux K.P. The human gut microbiome: current knowledge, challenges, and future directions. Transl. Res. 2012;160(4):246–257. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

