Complement activation is critical for placental ischemia-induced hypertension in the rat
- PMID: 23685261
- PMCID: PMC3687024
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molimm.2013.04.009
Complement activation is critical for placental ischemia-induced hypertension in the rat
Abstract
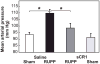
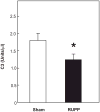
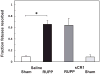
Preeclampsia is a major obstetric problem defined by new-onset hypertension and proteinuria associated with compromised placental perfusion. Although activation of the complement system is increased in preeclampsia compared to normal pregnancy, it remains unclear whether excess complement activation is a cause or consequence of placental ischemia. Therefore, we hypothesized that complement activation is critical for placental ischemia-induced hypertension. We employed the reduced utero-placental perfusion pressure (RUPP) model of placental ischemia in the rat to induce hypertension in the third trimester and evaluated the effect of inhibiting complement activation with a soluble recombinant form of an endogenous complement regulator, human complement receptor 1 (sCR1; CDX-1135). On day 14 of a 21-day gestation, rats received either RUPP or Sham surgery and 15 mg/kg/day sCR1 or saline intravenously on days 14-18. Circulating complement component 3 decreased and complement activation product C3a increased in RUPP vs. Sham (p<0.05), indicating complement activation had occurred. Mean arterial pressure (MAP) measured on day 19 increased in RUPP vs. Sham rats (109.8±2.8 mmHg vs. 93.6±1.6 mmHg). Treatment with sCR1 significantly reduced elevated MAP in RUPP rats (98.4±3.6 mmHg, p<0.05) and reduced C3a production. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) decreased in RUPP compared to Sham rats, and the decrease in VEGF was not affected by sCR1 treatment. Thus, these studies have identified a mechanistic link between complement activation and the pregnancy complication of hypertension apart from free plasma VEGF and have identified complement inhibition as a potential treatment strategy for placental ischemia-induced hypertension in preeclampsia.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Alexander BT, Kassab SE, Miller MT, Abram SR, Reckelhoff JF, Bennett WA, Granger JP. Reduced uterine perfusion pressure during pregnancy in the rat is associated with increases in arterial pressure and changes in renal nitric oxide. Hypertension. 2001;37:1191–5. - PubMed
-
- Baines MG, Millar KG, Mills P. Studies of complement levels in normal human pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 1974;43:806–10. - PubMed
-
- Baker PN, Krasnow J, Roberts JM, Yeo KT. Elevated serum levels of vascular endothelial growth factor in patients with preeclampsia. Obstet Gynecol. 1995;86:815–21. - PubMed
-
- Balta O, Boztosun A, Deveci K, Gulturk S, Ekici F, Kaya A, Cetin A, Cetin M. Reduced uterine perfusion pressure model is not successful to mimic severe preeclampsia. Placenta. 2011;32:675–80. - PubMed
-
- Buhimschi IA, Shi SQ, Saade GR, Garfield RE. Marked variation in responses to long-term nitric oxide inhibition during pregnancy in outbred rats from two different colonies. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2001;184:686–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

