Interleukin-6-signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 signaling mediates aortic dissections induced by angiotensin II via the T-helper lymphocyte 17-interleukin 17 axis in C57BL/6 mice
- PMID: 23685554
- PMCID: PMC3818154
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.301049
Interleukin-6-signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 signaling mediates aortic dissections induced by angiotensin II via the T-helper lymphocyte 17-interleukin 17 axis in C57BL/6 mice
Abstract
Objective: Dysregulated angiotensin II (Ang II) signaling induces local vascular interleukin-6 (IL-6) secretion, producing leukocyte infiltration and life-threatening aortic dissections. Precise mechanisms by which IL-6 signaling induces leukocyte recruitment remain unknown. T-helper 17 lymphocytes (Th17) have been implicated in vascular pathology, but their role in the development of aortic dissections is poorly understood. Here, we tested the relationship of IL-6-signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 signaling with Th17-induced inflammation in the formation of Ang II-induced dissections in C57BL/6 mice.
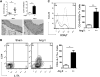
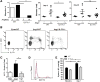
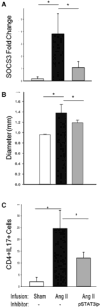
Approach and results: Ang II infusion induced aortic dissections and CD4(+)-interleukin 17A (IL-17A)-expressing Th17 cell accumulation in C57BL/6 mice. A blunted local Th17 activation, macrophage recruitment, and reduced incidence of aortic dissections were seen in IL-6(-/-) mice. To determine the pathological roles of Th17 lymphocytes, we treated Ang II-infused mice with IL-17A-neutralizing antibody or infused Ang II in genetically deficient IL-17A mice and found decreased aortic chemokine monocytic chemotactic protein-1 production and macrophage recruitment, leading to a reduction in aortic dissections. This effect was independent of blood pressure in IL-17A-neutralizing antibody experiment. Application of a cell-permeable signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 inhibitor to downregulate the IL-6 pathway decreased aortic dilation and Th17 cell recruitment. We also observed increased aortic Th17 infiltration and IL-17 mRNA expression in patients with thoracic aortic dissections. Finally, we found that Ang II-mediated aortic dissections occurred independent of blood pressure changes.
Conclusions: Our results indicate that the IL-6-signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 signaling pathway converges on Th17 recruitment and IL-17A signaling upstream of macrophage recruitment, mediating aortic dissections.
Keywords: T-lymphocytes, helper; angiotensin II; aortic dissection, familial; inflammation; interleukin-6; vascular inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures




Similar articles
-
An adventitial IL-6/MCP1 amplification loop accelerates macrophage-mediated vascular inflammation leading to aortic dissection in mice.J Clin Invest. 2009 Dec;119(12):3637-51. doi: 10.1172/JCI38308. Epub 2009 Nov 16. J Clin Invest. 2009. PMID: 19920349 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibiting the Th17/IL-17A-related inflammatory responses with digoxin confers protection against experimental abdominal aortic aneurysm.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014 Nov;34(11):2429-38. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.304435. Epub 2014 Sep 18. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014. PMID: 25234817
-
Smooth Muscle Cell-Derived Interleukin-17C Plays an Atherogenic Role via the Recruitment of Proinflammatory Interleukin-17A+ T Cells to the Aorta.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016 Aug;36(8):1496-506. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.307892. Epub 2016 Jun 30. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016. PMID: 27365405 Free PMC article.
-
[The molecular mechanisms contributing to the pathophysiology of systemic inflammatory response after acute aortic dissection].Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi. 2016;39(2):91-5. doi: 10.2177/jsci.39.91. Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi. 2016. PMID: 27212594 Review. Japanese.
-
Current views on the functions of interleukin-17A-producing cells in atherosclerosis.Thromb Haemost. 2011 Nov;106(5):787-95. doi: 10.1160/TH11-05-0342. Epub 2011 Sep 22. Thromb Haemost. 2011. PMID: 21946932 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of interleukin-6 in combination with D-dimer in predicting early poor postoperative prognosis after acute stanford type a aortic dissection.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2020 Jul 16;15(1):172. doi: 10.1186/s13019-020-01206-y. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2020. PMID: 32677975 Free PMC article.
-
The role of IL-6 in the physiologic versus hypertensive blood pressure actions of angiotensin II.Physiol Rep. 2015 Oct;3(10):e12595. doi: 10.14814/phy2.12595. Physiol Rep. 2015. PMID: 26486161 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of the NR4A nuclear receptor NOR1 in hematopoietic stem cells reduces inflammation but not abdominal aortic aneurysm formation.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2017 Oct 18;17(1):271. doi: 10.1186/s12872-017-0701-4. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2017. PMID: 29047330 Free PMC article.
-
Autonomic regulation of the immune system in cardiovascular diseases.Adv Physiol Educ. 2017 Dec 1;41(4):578-593. doi: 10.1152/advan.00061.2017. Adv Physiol Educ. 2017. PMID: 29138216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Independent and Interactive Roles of Immunity and Metabolism in Aortic Dissection.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 2;24(21):15908. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115908. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958896 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schluter KD, Wenzel S. Angiotensin ii: A hormone involved in and contributing to pro-hypertrophic cardiac networks and target of anti-hypertrophic cross-talks. Pharmacology & therapeutics. 2008;119:311–325. - PubMed
-
- He R, Guo DC, Estrera AL, Safi HJ, Huynh TT, Yin Z, Cao SN, Lin J, Kurian T, Buja LM, Geng YJ, Milewicz DM. Characterization of the inflammatory and apoptotic cells in the aortas of patients with ascending thoracic aortic aneurysms and dissections. The Journal of thoracic and cardiovascular surgery. 2006;131:671–678. - PubMed
-
- Daugherty A, Cassis LA. Mechanisms of abdominal aortic aneurysm formation. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2002;4:222–227. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

