Broadband homonuclear correlation spectroscopy driven by combined R2(n)(v) sequences under fast magic angle spinning for NMR structural analysis of organic and biological solids
- PMID: 23685715
- PMCID: PMC3703537
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmr.2013.04.009
Broadband homonuclear correlation spectroscopy driven by combined R2(n)(v) sequences under fast magic angle spinning for NMR structural analysis of organic and biological solids
Abstract
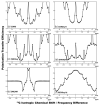
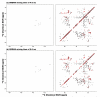
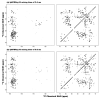
We recently described a family of experiments for R2n(v) Driven Spin Diffusion (RDSD) spectroscopy suitable for homonuclear correlation experiments under fast MAS conditions [G. Hou, S. Yan, S.J. Sun, Y. Han, I.J. Byeon, J. Ahn, J. Concel, A. Samoson, A.M. Gronenborn, T. Polenova, Spin diffusion drive by R-symmetry sequencs: applications to homonuclear correlation spectroscopy in MAS NMR of biological and organic solids, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133 (2011) 3943-3953]. In these RDSD experiments, since the broadened second-order rotational resonance conditions are dominated by the radio frequency field strength and the phase shifts, as well as the size of reintroduced dipolar couplings, the different R2n(v) sequences display unique polarization transfer behaviors and different recoupling frequency bandwidths. Herein, we present a series of modified R2n(v) sequences, dubbed COmbined R2n(v)-Driven (CORD), that yield broadband homonuclear dipolar recoupling and give rise to uniform distribution of cross peak intensities across the entire correlation spectrum. We report NMR experiments and numerical simulations demonstrating that these CORD spin diffusion sequences are suitable for broadband recoupling at a wide range of magnetic fields and MAS frequencies, including fast-MAS conditions (νr=40 kHz and above). Since these CORD sequences are largely insensitive to dipolar truncation, they are well suited for the determination of long-range distance constraints, which are indispensable for the structural characterization of a broad range of systems. Using U-(13)C,(15)N-alanine and U-(13)C,(15)N-histidine, we show that under fast-MAS conditions, the CORD sequences display polarization transfer efficiencies within broadband frequency regions that are generally higher than those offered by other existing spin diffusion pulse schemes. A 89-residue U-(13)C,(15)N-dynein light chain (LC8) protein has also been used to demonstrate that the CORD sequences exhibit uniformly high cross peak intensities across the entire chemical shift range.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Combined zero-quantum and spin-diffusion mixing for efficient homonuclear correlation spectroscopy under fast MAS: broadband recoupling and detection of long-range correlations.J Biomol NMR. 2015 Jan;61(1):7-20. doi: 10.1007/s10858-014-9875-6. Epub 2014 Nov 25. J Biomol NMR. 2015. PMID: 25420598 Free PMC article.
-
Recoupling of chemical shift anisotropy by R-symmetry sequences in magic angle spinning NMR spectroscopy.J Chem Phys. 2012 Oct 7;137(13):134201. doi: 10.1063/1.4754149. J Chem Phys. 2012. PMID: 23039592 Free PMC article.
-
Spin diffusion driven by R-symmetry sequences: applications to homonuclear correlation spectroscopy in MAS NMR of biological and organic solids.J Am Chem Soc. 2011 Mar 23;133(11):3943-53. doi: 10.1021/ja108650x. Epub 2011 Mar 1. J Am Chem Soc. 2011. PMID: 21361320 Free PMC article.
-
Recent progress in dipolar recoupling techniques under fast MAS in solid-state NMR spectroscopy.Solid State Nucl Magn Reson. 2021 Apr;112:101711. doi: 10.1016/j.ssnmr.2020.101711. Epub 2021 Jan 11. Solid State Nucl Magn Reson. 2021. PMID: 33508579 Review.
-
Homonuclear dipolar recoupling techniques for structure determination in uniformly 13C-labeled proteins.Solid State Nucl Magn Reson. 2009 Nov;36(3):119-28. doi: 10.1016/j.ssnmr.2009.07.003. Epub 2009 Aug 5. Solid State Nucl Magn Reson. 2009. PMID: 19729285 Review.
Cited by
-
Pulsed Third-Spin-Assisted Recoupling NMR for Obtaining Long-Range 13C-13C and 15N-13C Distance Restraints.J Phys Chem B. 2020 Aug 20;124(33):7138-7151. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.0c04574. Epub 2020 Aug 6. J Phys Chem B. 2020. PMID: 32700540 Free PMC article.
-
Measurement of Accurate Interfluorine Distances in Crystalline Organic Solids: A High-Frequency Magic Angle Spinning NMR Approach.J Phys Chem B. 2019 Dec 19;123(50):10680-10690. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.9b08919. Epub 2019 Dec 10. J Phys Chem B. 2019. PMID: 31682453 Free PMC article.
-
pH- and Calcium-Dependent Aromatic Network in the SARS-CoV-2 Envelope Protein.J Am Chem Soc. 2022 Apr 20;144(15):6839-6850. doi: 10.1021/jacs.2c00973. Epub 2022 Apr 5. J Am Chem Soc. 2022. PMID: 35380805 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging active site chemistry and protonation states: NMR crystallography of the tryptophan synthase α-aminoacrylate intermediate.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Jan 11;119(2):e2109235119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2109235119. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 34996869 Free PMC article.
-
From Angstroms to Nanometers: Measuring Interatomic Distances by Solid-State NMR.Chem Rev. 2022 May 25;122(10):9848-9879. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00662. Epub 2021 Oct 25. Chem Rev. 2022. PMID: 34694769 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nishimura K, Kim S, Zhang L, Cross TA. The closed state of a H+ channel helical bundle combining precise orientational and distance restraints from solid state NMR. Biochemistry. 2002;41:13170–13177. - PubMed
-
- Tycko R. Applications of solid state NMR to the structural characterization of amyloid fibrils: methods and results. Prog. Nucl. Mag. Reson. Spectr. 2003;42:53–68.
-
- Franks WT, Wylie BJ, Stellfox SA, Rienstra CM. Backbone conformational constraints in a microcrystalline U-15N-labeled protein by 3D dipolar-shift solid-state NMR spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006;128:3154–3155. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

