From neural signatures of emotional modulation to social cognition: individual differences in healthy volunteers and psychiatric participants
- PMID: 23685775
- PMCID: PMC4090956
- DOI: 10.1093/scan/nst067
From neural signatures of emotional modulation to social cognition: individual differences in healthy volunteers and psychiatric participants
Abstract
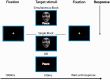
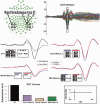
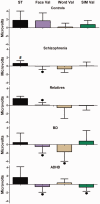
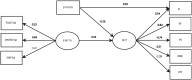
It is commonly assumed that early emotional signals provide relevant information for social cognition tasks. The goal of this study was to test the association between (a) cortical markers of face emotional processing and (b) social-cognitive measures, and also to build a model which can predict this association (a and b) in healthy volunteers as well as in different groups of psychiatric patients. Thus, we investigated the early cortical processing of emotional stimuli (N170, using a face and word valence task) and their relationship with the social-cognitive profiles (SCPs, indexed by measures of theory of mind, fluid intelligence, speed processing and executive functions). Group comparisons and individual differences were assessed among schizophrenia (SCZ) patients and their relatives, individuals with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), individuals with euthymic bipolar disorder (BD) and healthy participants (educational level, handedness, age and gender matched). Our results provide evidence of emotional N170 impairments in the affected groups (SCZ and relatives, ADHD and BD) as well as subtle group differences. Importantly, cortical processing of emotional stimuli predicted the SCP, as evidenced by a structural equation model analysis. This is the first study to report an association model of brain markers of emotional processing and SCP.
Keywords: ADHD; BD; N170; SEM; schizophrenia; social cognition.
© The Author (2013). Published by Oxford University Press. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cortical deficits of emotional face processing in adults with ADHD: its relation to social cognition and executive function.Soc Neurosci. 2011;6(5-6):464-81. doi: 10.1080/17470919.2011.620769. Epub 2011 Oct 3. Soc Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21961874
-
Neural processing of emotional facial and semantic expressions in euthymic bipolar disorder (BD) and its association with theory of mind (ToM).PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e46877. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046877. Epub 2012 Oct 8. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23056505 Free PMC article.
-
An ERP Study of Face Processing in Schizophrenia, Bipolar Disorder, and Socially Isolated Individuals from the Community.Clin EEG Neurosci. 2024 Jul;55(4):395-405. doi: 10.1177/15500594231222979. Epub 2024 Jan 31. Clin EEG Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38298008 Free PMC article.
-
N170 in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: Systematic review.Int J Psychophysiol. 2025 Jul;213:112585. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2025.112585. Epub 2025 May 9. Int J Psychophysiol. 2025. PMID: 40349985
-
Cognitive deficits in bipolar disorders: Implications for emotion.Clin Psychol Rev. 2018 Feb;59:126-136. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2017.11.006. Epub 2017 Nov 21. Clin Psychol Rev. 2018. PMID: 29195773 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ERP Correlates of Proactive and Reactive Cognitive Control in Treatment-Naïve Adult ADHD.PLoS One. 2016 Jul 22;11(7):e0159833. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0159833. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27448275 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropsychology, social cognition and global functioning among bipolar, schizophrenic patients and healthy controls: preliminary data.Front Hum Neurosci. 2013 Oct 17;7:661. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2013.00661. eCollection 2013. Front Hum Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24146642 Free PMC article.
-
The Latin America and the Caribbean Consortium on Dementia (LAC-CD): From Networking to Research to Implementation Science.J Alzheimers Dis. 2021;82(s1):S379-S394. doi: 10.3233/JAD-201384. J Alzheimers Dis. 2021. PMID: 33492297 Free PMC article.
-
How do you feel when you can't feel your body? Interoception, functional connectivity and emotional processing in depersonalization-derealization disorder.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 26;9(6):e98769. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0098769. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24967634 Free PMC article.
-
What makes the dorsomedial frontal cortex active during reading the mental states of others?Front Neurosci. 2013 Dec 5;7:232. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2013.00232. Front Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24367287 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

