Nucleolar control of p53: a cellular Achilles' heel and a target for cancer therapy
- PMID: 23685903
- PMCID: PMC11113510
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-013-1361-x
Nucleolar control of p53: a cellular Achilles' heel and a target for cancer therapy
Abstract
Nucleoli perform a crucial cell function, ribosome biogenesis, and of critical relevance to the subject of this review, they are also extremely sensitive to cellular stresses, which can cause loss of function and/or associated structural disruption. In recent years, we have learned that cells take advantage of this stress sensitivity of nucleoli, using them as stress sensors. One major protein regulated by this role of nucleoli is the tumor suppressor p53, which is activated in response to diverse cellular injuries in order to exert its onco-protective effects. Here we discuss a model of nucleolar regulation of p53, which proposes that key steps in the promotion of p53 degradation by the ubiquitin ligase MDM2 occur in nucleoli, thus providing an explanation for the observed link between nucleolar disruption and p53 stability. We review current evidence for this compartmentalization in p53 homeostasis and highlight current limitations of the model. Interestingly, a number of current chemotherapeutic agents capable of inducing a p53 response are likely to do so by targeting nucleolar functions and these compounds may serve to inform further improved therapeutic targeting of nucleoli.
Figures
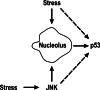

References
-
- von Bertalanffy L. Problems of life: an evaluation of modern biological and scientific thought. New York: Harper; 1960.
-
- Vazquez A, Bond EE, Levine AJ, Bond GL. The genetics of the p53 pathway, apoptosis and cancer therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008;7(12):979–987. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

