Penoscrotal extramammary Paget's disease: surgical techniques and follow-up experiences with thirty patients
- PMID: 23685910
- PMCID: PMC3739235
- DOI: 10.1038/aja.2013.27
Penoscrotal extramammary Paget's disease: surgical techniques and follow-up experiences with thirty patients
Abstract
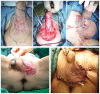
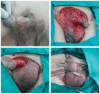
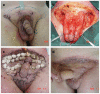
To report the surgical management, complications and prognosis of patients with penoscrotal extramammary Paget's disease (EMPD) at different clinical stages. Between 2003 and 2008, a total of 30 male patients with penoscrotal EMPD were enrolled and evaluated. All enrolled subjects received frozen biopsy-guided local wide resection and immediate reconstruction. Patients were followed every 3 months postoperatively. Among the 30 patients who accepted and underwent frozen biopsy-guided local wide resection treatment and reconstruction, two (6.7%) cases exhibited positive margins, verified by pathological examination, and underwent re-excision after surgery. The technique of primary closure or an adjacent flap was used in 10 (33.3%) cases, split-thickness skin grafts were used in 15 (50%), and an anterolateral thigh perforator flap was used in five cases (16.7%). The postoperative complications were acceptable. The mean follow-up time was 64.9 ± 29.6 months. Of all 30 cases, 22 patients (73.3%) survived with no evidence of recurrence, four patients (13.3%) exhibited local recurrence, two patients (6.7%) exhibited both local recurrence and distant metastasis and the remaining two patients (6.7%) exhibited distant metastasis. Five patients died from metastasis or cachexia. Current surgical techniques, including primary closure, adjacent flaps, split-thickness skin flaps and anterolateral thigh perforator flaps are able to reconstruct all types of defects with acceptable complications. Some patients with negative margins went on to exhibit local recurrence, potentially due to adnexal carcinoma or internal malignancy.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Superficial circumflex iliac artery perforator propeller flap for penoscrotal extramammary Paget's disease.Int J Dermatol. 2025 Jan;64(1):142-148. doi: 10.1111/ijd.17325. Epub 2024 Jul 15. Int J Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 39010187
-
Reconstruction with scrotal skin flaps after wide local resection of penoscrotal extramammary Paget's disease.BJU Int. 2012 Dec;110(11 Pt C):E1121-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2012.11491.x. Epub 2012 Sep 18. BJU Int. 2012. PMID: 22985467
-
Extramammary Paget's disease of the penis and scrotum: excision, reconstruction and evaluation of occult malignancy.J Urol. 2001 Dec;166(6):2112-6; discussion 2117. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(05)65516-4. J Urol. 2001. PMID: 11696717
-
Extramammary Paget's Disease of the Scrotal and Penile: A Case Report and Review of the Literature.Urol Int. 2024;108(3):264-271. doi: 10.1159/000536654. Epub 2024 Feb 17. Urol Int. 2024. PMID: 38368870 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic efficacy of combined superficial circumflex iliac artery perforator flap and bilateral pedicled scrotal flaps for perineal defects in male patients with extramammary Paget's disease.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2025 Apr;103:333-341. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2024.09.036. Epub 2024 Sep 18. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2025. PMID: 40054293 Review.
Cited by
-
An Important Differential: Extramammary Paget's Disease.Eplasty. 2015 Mar 12;15:ic16. eCollection 2015. Eplasty. 2015. PMID: 25834696 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Transcriptome sequencing reveals a lncRNA-mRNA interaction network in extramammary Paget's disease.BMC Med Genomics. 2021 Dec 11;14(1):291. doi: 10.1186/s12920-021-01135-2. BMC Med Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34895219 Free PMC article.
-
Pemetrexed induced a durable response in heavily pretreated metastatic extramammary Paget's disease.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Jun 15;8(6):9595-8. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26309631 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstruction With Pedicled Anterolateral Thigh Flap After Wide Local Excision of Penoscrotal Extramammary Paget's Disease: A Case Report and Comprehensive Literature Review.Eplasty. 2015 Jun 24;15:e26. eCollection 2015. Eplasty. 2015. PMID: 26171098 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor Wide Horizontal Invasion Predicts Local Recurrence for Scrotal Extramammary Paget's Disease.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 21;7:44933. doi: 10.1038/srep44933. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28322288 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee KY, Roh MR, Chung WG, Chung KY. Comparison of Mohs micrographic surgery and wide excision for extramammary Paget's Disease: Korean experience. Dermatol Surg. 2009;35:34–40. - PubMed
-
- Hatta N, Yamada M, Hirano T, Fujimoto A, Morita R. Extramammary Paget's disease: treatment, prognostic factors and outcome in 76 patients. Br J Dermatol. 2008;158:313–8. - PubMed
-
- Wang Z, Lu M, Dong GQ, Jiang YQ, Lin MS, et al. Penile and scrotal Paget's disease: 130 Chinese patients with long-term follow-up. BJU Int. 2008;102:485–8. - PubMed
-
- Mochitomi Y, Sakamoto R, Gushi A, Hashiguchi T, Mera K, et al. Extramammary Paget's disease/carcinoma successfully treated with a combination chemotherapy: report of two cases. J Dermatol. 2005;32:632–7. - PubMed
-
- Luk NM, Yu KH, Yeung WK, Choi CL, Teo ML. Extramammary Paget's disease: outcome of radiotherapy with curative intent. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2003;28:360–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

