IL-1α signaling initiates the inflammatory response to virulent Legionella pneumophila in vivo
- PMID: 23686480
- PMCID: PMC3682686
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1300100
IL-1α signaling initiates the inflammatory response to virulent Legionella pneumophila in vivo
Abstract
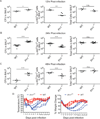
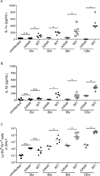
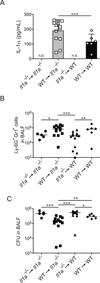
Legionella pneumophila is an intracellular bacterial pathogen that is the cause of a severe pneumonia in humans called Legionnaires' disease. A key feature of L. pneumophila pathogenesis is the rapid influx of neutrophils into the lungs, which occurs in response to signaling via the IL-1R. Two distinct cytokines, IL-1α and IL-1β, can stimulate the type I IL-1R. IL-1β is produced upon activation of cytosolic sensors called inflammasomes that detect L. pneumophila in vitro and in vivo. Surprisingly, we find no essential role for IL-1β in neutrophil recruitment to the lungs in response to L. pneumophila. Instead, we show that IL-1α is a critical initiator of neutrophil recruitment to the lungs of L. pneumophila-infected mice. We find that neutrophil recruitment in response to virulent L. pneumophila requires the production of IL-1α specifically by hematopoietic cells. In contrast to IL-1β, the innate signaling pathways that lead to the production of IL-1α in response to L. pneumophila remain poorly defined. In particular, although we confirm a role for inflammasomes for initiation of IL-1β signaling in vivo, we find no essential role for inflammasomes in production of IL-1α. Instead, we propose that a novel host pathway, perhaps involving inhibition of host protein synthesis, is responsible for IL-1α production in response to virulent L. pneumophila. Our results establish IL-1α as a critical initiator of the inflammatory response to L. pneumophila in vivo and point to an important role for IL-1α in providing an alternative to inflammasome-mediated immune responses in vivo.
Figures



References
-
- Fontana MF, Vance RE. Two signal models in innate immunity. Immunol Rev. 2011;243:26–39. - PubMed
-
- Winn WC, Jr, Myerowitz RL. The pathology of the Legionella pneumonias. A review of 74 cases and the literature. Human pathology. 1981;12:401–422. - PubMed
-
- Trisolini R, Lazzari Agli L, Cancellieri A, Procaccio L, Candoli P, Alifano M, Patelli M. Bronchoalveolar lavage findings in severe community-acquired pneumonia due to Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1. Respir Med. 2004;98:1222–1226. - PubMed
-
- Yu H, Higa F, Koide M, Haranaga S, Yara S, Tateyama M, Li H, Fujita J. Lung abscess caused by Legionella species: implication of the immune status of hosts. Intern Med. 2009;48:1997–2002. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

