Warm temperatures induce transgenerational epigenetic release of RNA silencing by inhibiting siRNA biogenesis in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 23686579
- PMCID: PMC3670308
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1219655110
Warm temperatures induce transgenerational epigenetic release of RNA silencing by inhibiting siRNA biogenesis in Arabidopsis
Abstract
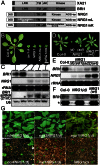
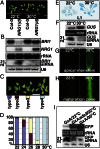
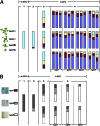
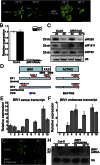
Owing to their sessile nature, plants have evolved sophisticated genetic and epigenetic regulatory systems to respond quickly and reversibly to daily and seasonal temperature changes. However, our knowledge of how plants sense and respond to warming ambient temperatures is rather limited. Here we show that an increase in growth temperature from 22 °C to 30 °C effectively inhibited transgene-induced posttranscriptional gene silencing (PTGS) in Arabidopsis. Interestingly, warmth-induced PTGS release exhibited transgenerational epigenetic inheritance. We discovered that the warmth-induced PTGS release occurred during a critical step that leads to the formation of double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) for producing small interfering RNAs (siRNAs). Deep sequencing of small RNAs and RNA blot analysis indicated that the 22-30 °C increase resulted in a significant reduction in the abundance of many trans-acting siRNAs that require dsRNA for biogenesis. We discovered that the temperature increase reduced the protein abundance of SUPPRESSOR OF GENE SILENCING 3, as a consequence, attenuating the formation of stable dsRNAs required for siRNA biogenesis. Importantly, SUPPRESSOR OF GENE SILENCING 3 overexpression released the warmth-triggered inhibition of siRNA biogenesis and reduced the transgenerational epigenetic memory. Thus, our study reveals a previously undescribed association between warming temperatures, an epigenetic system, and siRNA biogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Long SP, Ort DR. More than taking the heat: Crops and global change. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2010;13(3):241–248. - PubMed
-
- Lobell DB, Field CB. Global scale climate–crop yield relationships and the impacts of recent warming. Environ Res Lett. 2007;2(1):014002.
-
- Blázquez MA, Ahn JH, Weigel D. A thermosensory pathway controlling flowering time in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat Genet. 2003;33(2):168–171. - PubMed
-
- Lin L, Zhong SH, Cui XF, Li J, He ZH. Characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants reveals a role for receptor-like kinase SCRAMBLED/STRUBBELIG in coordinating cell proliferation and differentiation during Arabidopsis leaf development. Plant J. 2012;72(5):707–720. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

