Mechanisms of cardiovascular actions of urocortins in the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus of the rat
- PMID: 23686711
- PMCID: PMC3726959
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00138.2013
Mechanisms of cardiovascular actions of urocortins in the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus of the rat
Abstract
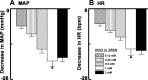
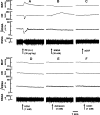
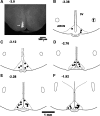
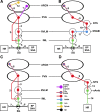
The presence of urocortins (UCNs) and corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) receptors has been reported in the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus (ARCN). We have previously reported that UCNs are involved in central cardiovascular regulation. Based on this information, we hypothesized that the ARCN may be one of the sites where UCNs exert their central cardiovascular actions. Experiments were done in artificially ventilated, adult male Wistar rats anesthetized with urethane. Unilateral microinjections (30 nl) of UCN1 (0.12-2 mM) elicited decreases in mean arterial pressure (MAP) and heart rate (HR). Maximum cardiovascular responses were elicited by a 1 mM concentration of UCN1. Microinjections of UCN2 and UCN3 (1 mM each) into the ARCN elicited similar decreases in MAP and HR. UCN1 was used as a prototype for the other experiments described below. HR responses elicited by UCN1 were significantly attenuated by bilateral vagotomy. Prior microinjections of NBI-27914 (CRF-1 receptor antagonist) and astressin (CRF-1 receptor and CRF-2 receptor antagonist) (1 mM each) into the ARCN significantly attenuated the cardiovascular responses elicited by UCN1 microinjections at the same site. Microinjections of UCN1 into the ARCN decreased efferent renal sympathetic nerve activity. It was concluded that microinjections of UCN1, UCN2, and UCN3 into the ARCN elicited decreases in MAP and HR. Decreases in MAP, HR, and renal sympathetic nerve activity elicited by UCN1 microinjections into the ARCN were mediated via CRF receptors. Bradycardic responses to UCN1 were mediated via the activation of vagus nerves, and decreases in MAP may be mediated via decreases in sympathetic nerve activity.
Keywords: N-methyl-d-aspartic acid; blood pressure; heart rate; microinjection; sympathetic nerve activity.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cardiovascular responses to hypothalamic arcuate nucleus stimulation in the rat: role of sympathetic and vagal efferents.Hypertension. 2009 Dec;54(6):1369-75. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.109.140715. Epub 2009 Nov 2. Hypertension. 2009. PMID: 19884562
-
Effect of barodenervation on cardiovascular responses elicited from the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus of the rat.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e53111. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053111. Epub 2012 Dec 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23300873 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular responses to microinjections of urocortin 3 into the nucleus tractus solitarius of the rat.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2009 Feb;296(2):H325-32. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.01044.2008. Epub 2008 Dec 5. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19060121 Free PMC article.
-
Urocortins: CRF's siblings and their potential role in anxiety, depression and alcohol drinking behavior.Alcohol. 2012 Jun;46(4):349-57. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2011.10.007. Epub 2012 Mar 22. Alcohol. 2012. PMID: 22444954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of urocortins in the cardiovascular system.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2014 Dec;65(6):753-66. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25554979 Review.
Cited by
-
Corticotropin releasing factor excites neurons of posterior hypothalamic nucleus to produce tachycardia in rats.Sci Rep. 2016 Feb 1;6:20206. doi: 10.1038/srep20206. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26831220 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Downregulation of Urocortin Expression in the Hypothalamo-Neurohypophysial System of Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats.Front Physiol. 2021 Mar 17;11:599507. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.599507. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33815127 Free PMC article.
-
A molecular census of arcuate hypothalamus and median eminence cell types.Nat Neurosci. 2017 Mar;20(3):484-496. doi: 10.1038/nn.4495. Epub 2017 Feb 6. Nat Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28166221 Free PMC article.
-
Liver vitronectin release into the bloodstream increases due to reduced vagal muscarinic signaling after cerebral stroke in female mice.Physiol Rep. 2022 May;10(9):e15301. doi: 10.14814/phy2.15301. Physiol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35531929 Free PMC article.
-
GABA and glycine receptors in the nucleus ambiguus mediate tachycardia elicited by chemical stimulation of the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015 Jul 1;309(1):H174-84. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00801.2014. Epub 2015 May 8. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25957221 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aguilera G, Nikodemova M, Wynn PC, Catt KJ. Corticotropin releasing hormone receptors: two decades later. Peptides 25: 319–329, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Baffi JS, Palkovits M. Fine topography of brain areas activated by cold stress. A fos immunohistochemical study in rats. Neuroendocrinology 72: 102–113, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Bedi M, Varshney VP, Babbar R. Role of cardiovascular reactivity to mental stress in predicting future hypertension. Clin Exp Hypertens 22: 1–22, 2000 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

