Oral and Intravenous Acetylcysteine for Treatment of Acetaminophen Toxicity: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- PMID: 23687539
- PMCID: PMC3656701
- DOI: 10.5811/westjem.2012.4.6885
Oral and Intravenous Acetylcysteine for Treatment of Acetaminophen Toxicity: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Abstract
Introduction: There are few reports summarizing the effectiveness of oral and intravenous (IV) acetylcysteine. We determined the proportion of acetaminophen poisoned patients who develop hepatotoxicity (serum transaminase > 1000 IU/L) when treated with oral and IV acetylcysteine.
Methods: Studies were double abstracted by trained researchers. We determined the proportions of patients who developed hepatotoxicity for each route using a random effects model. Studies were further stratified by early and late treatment.
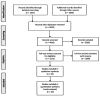
Results: We screened 4,416 abstracts; 16 articles, including 5,164 patients, were included in the meta-analysis. The overall rate of hepatotoxicity for the oral and IV routes were 12.6% and 13.2%, respectively. Treatment delays are associated with a higher rate of hepatotoxicity.
Conclusion: Studies report similar rates of hepatotoxicity for oral and IV acetylcysteine, but direct comparisons are lacking. While it is difficult to disentangle the effects of dose and duration from route, our findings suggest that the rates of hepatotoxicity are similar for oral and IV administration.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Comment in
-
Is intravenous acetylcysteine more effective than oral administration for the prevention of hepatotoxicity in acetaminophen overdose?Ann Emerg Med. 2014 Jan;63(1):79-80. doi: 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2013.07.002. Epub 2013 Aug 5. Ann Emerg Med. 2014. PMID: 23927960 No abstract available.
References
-
- Manthripragada AD, Zhou EH, Budnitz DS. Characterization of acetaminophen overdose-related emergency department visits and hospitalizations in the United States. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2011;20(8):819–826. et al. - PubMed
-
- Prescott LF, Park J, Ballantyne A. Treatment of paracetamol (acetaminophen) poisoning with N-acetylcysteine. Lancet. 1977;2(8035):432–434. et al. - PubMed
-
- Smilkstein MJ, Knapp GL, Kulig KW. Efficacy of oral N-acetylcysteine in the treatment of acetaminophen overdose. Analysis of the national multicenter study (1976 to 1985) N Eng J Med. 1988;319(24):1557–1562. et al. - PubMed
-
- Bronstein AC, Spyker DA, Cantilena LR. 2009 Annual Report of the American Association of Poison Control Centers' National Poison Data System (NPDS): 27th Annual Report. Clin Toxicol (Phila) 2010;48(10):979–1178. et al. - PubMed
-
- Brok J, Buckley N, Gluud C. Interventions for paracetamol (acetaminophen) overdose. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006;2006(2):CD003328. - PubMed

