A Computational Study of the Origin of Stereoinduction in NHC-Catalyzed Annulation Reactions of α,β-Unsaturated Acyl Azoliums
- PMID: 23687566
- PMCID: PMC3655779
- DOI: 10.1039/C2SC20331F
A Computational Study of the Origin of Stereoinduction in NHC-Catalyzed Annulation Reactions of α,β-Unsaturated Acyl Azoliums
Abstract
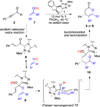
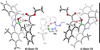
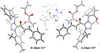
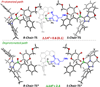
The origin of stereoselectivity of NHC-catalyzed annulation reactions of ynals and stable enols was studied with Density Functional Theory. The data suggest that the C-C bond formation is the stereo-determining step. Only the deprotonated pathway (containing an oxy anion and overall neutral species) was found to give rise to discrimination of the competing stereoisomers. This is due predominantly to electrostatic repulsion of the β-stabilizing enolate functionality with the π-cloud of the aryl group in the NHC-catalyst.
Figures

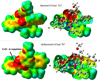
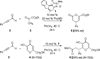
Similar articles
-
On the mechanism of N-heterocyclic carbene-catalyzed reactions involving acyl azoliums.Acc Chem Res. 2014 Feb 18;47(2):696-707. doi: 10.1021/ar400239v. Epub 2014 Jan 10. Acc Chem Res. 2014. PMID: 24410291
-
A DFT study of the mechanism of NHC catalysed annulation reactions involving α,β-unsaturated acyl azoliums and β-naphthol.Org Biomol Chem. 2016 Sep 21;14(35):8338-45. doi: 10.1039/c6ob01442a. Epub 2016 Aug 17. Org Biomol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27530598
-
A DFT study on the NHC catalysed Michael addition of enols to α,β-unsaturated acyl-azoliums. A base catalysed C-C bond-formation step.Org Biomol Chem. 2014 Feb 14;12(6):895-904. doi: 10.1039/c3ob41924j. Org Biomol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24343422
-
N-Heterocyclic Carbene Catalysis via Azolium Dienolates: An Efficient Strategy for Remote Enantioselective Functionalizations.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2018 Apr 3;57(15):3862-3873. doi: 10.1002/anie.201709684. Epub 2018 Mar 9. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2018. PMID: 29136320 Review.
-
Bifunctional N-Heterocyclic Carbenes Derived from l-Pyroglutamic Acid and Their Applications in Enantioselective Organocatalysis.Acc Chem Res. 2020 Mar 17;53(3):690-702. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00635. Epub 2020 Mar 6. Acc Chem Res. 2020. PMID: 32142245 Review.
Cited by
-
Post-Transition-State Dynamic Effects in the Transmetalation of Pd(II)-F to Pd(II)-CF3.JACS Au. 2023 Dec 29;4(1):263-275. doi: 10.1021/jacsau.3c00724. eCollection 2024 Jan 22. JACS Au. 2023. PMID: 38274253 Free PMC article.
-
Catalytic Kinetic Resolution of a Dynamic Racemate: Highly Stereoselective β-Lactone Formation by N-Heterocyclic Carbene Catalysis.Chem Sci. 2014 May 1;5(5):1974-1982. doi: 10.1039/C4SC00317A. Chem Sci. 2014. PMID: 25045464 Free PMC article.
-
Organocatalytic Reactions Enabled by N-Heterocyclic Carbenes.Chem Rev. 2015 Sep 9;115(17):9307-87. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00060. Epub 2015 May 20. Chem Rev. 2015. PMID: 25992594 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative N-Heterocyclic Carbene Catalysis.Chemistry. 2023 Jan 18;29(4):e202202467. doi: 10.1002/chem.202202467. Epub 2022 Nov 22. Chemistry. 2023. PMID: 36205918 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Incorporation of redox-inactive cations promotes iron catalyzed aerobic C-H oxidation at mild potentials.Chem Sci. 2018 Feb 7;9(9):2567-2574. doi: 10.1039/c7sc04486k. eCollection 2018 Mar 7. Chem Sci. 2018. PMID: 29732136 Free PMC article.
References
-
-
For general reviews of NHC chemistry, see Nair V, Menon RS, Biju AT, Sinu CR, Paul RR, Jose A, Sreekumar V. Tetrahedron. 2011;67:9885. Chiang P-C, Bode JW. N-Heterocyclic Carbenes; The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2011:399–435. Moore JL, Rovis, T. T. Top. Curr. Chem.; B. List, Ed. Vol. 291. Springer; 2009. pp. 77–144. Nair V, Vellalath S, Babu BP. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008;37:2691–2698. Enders D, Niemeier O, Henseler A. Chem. Rev. 2007;107:5606.
-
-
- Mahatthananchai J, Zheng P, Bode JW. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011;50:1673. - PMC - PubMed
- Mahatthananchai J, Bode JW. Chem. Sci. 2012;3:192. - PMC - PubMed
- Kaeobamrung J, Mahatthananchai J, Zheng P, Bode JW. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010;132:8810. - PMC - PubMed
- Mahatthananchai J, Kaeobamrung J, Bode JW. ACS Catalysis. 2012;2:494. - PMC - PubMed
-
-
Ryan SJ, Candish L, Lupton DW. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009;131:14176. Candish L, Lupton DW. Org. Lett. 2010;12:4836. Ryan SJ, Candish L, Lupton DW. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011;133:4694. d) for mechanistic and computational studies: Ryan SJ, Stasch A, Paddon-Row MN, Lupton DW. J. Org. Chem. 2012;77:1113.
-
-
- Zhu ZQ, Xiao JC. Adv. Syn. Catal. 2010;352:2455–2458.
- Zhu ZQ, Zheng X-L, Jiang N-F, Wan X, Xiao J-C. Chem. Commun. 2011;47:8670–8672. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

