X-ray irradiation promotes apoptosis of hippocampal neurons through up-regulation of Cdk5 and p25
- PMID: 23688022
- PMCID: PMC3673899
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2867-13-47
X-ray irradiation promotes apoptosis of hippocampal neurons through up-regulation of Cdk5 and p25
Abstract
Background: Cranial radiation therapy has been used for the treatment of primary and metastatic brain tumors. A prominent feature of brain injury induced by the radiation therapy is hippocampal dysfunction, characterized by a decline in memory. Cdk5 plays an important role in memory formation. Abnormal Cdk5 activity is associated with neuronal apoptosis induced by neurotoxic stimuli. However, the roles of Cdk5 in hippocampal apoptosis in response to X-ray irradiation have not been explored.
Methods: The expression of Cdk5 activators, p35 and p25, in hippocampal neurons was tested in both in vivo animal and in vitro couture after X-ray irradiation.
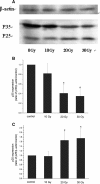
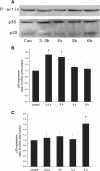
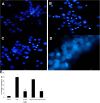
Results: After X-ray irradiation at 20 Gy and 30 Gy in rats, the number of hippocampal neuronal pyknosis was increased, but the number of hippocampal neuron was decreased, in the hippocampal CA1 region of rats. In these animals undergone with X-ray irradiation, the expression of p35 was significantly down-regulated, but it was up-regulated in p25. These opposite expressions were also shown in the primary cultured hippocampal neurons with 30 Gy irradiation. The apoptosis induced by X-ray irradiation were significantly prevented by the pretreatment of Cdk5 inhibitor, roscovitine, in both in vivo and in vitro settings.
Conclusions: X-ray irradiation resulted in a hippocampal neuronal apoptosis through up-regulation of p25, the Cdk5 activator. Hyperactivity of Cdk5 was involved in the pathogenesis of X-ray irradiation-induced hippocampal neuronal apoptosis. Blockade of Cdk5 signal pathway effectively protected neurons from the irradiation-induced brain injury.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[p35 and p25 expressions and Cdk5 kinase activity in primary cultured rat hippocampal neurons with X-ray exposure].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2009 Mar;29(3):405-7. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2009. PMID: 19304511 Chinese.
-
Calpain-2/p35-p25/Cdk5 pathway is involved in the neuronal apoptosis induced by polybrominated diphenyl ether-153.Toxicol Lett. 2017 Aug 5;277:41-53. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2017.05.027. Epub 2017 May 27. Toxicol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28559121
-
A 24-residue peptide (p5), derived from p35, the Cdk5 neuronal activator, specifically inhibits Cdk5-p25 hyperactivity and tau hyperphosphorylation.J Biol Chem. 2010 Oct 29;285(44):34202-12. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.134643. Epub 2010 Aug 18. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20720012 Free PMC article.
-
The regulation of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activity through the metabolism of p35 or p39 Cdk5 activator.Neurosignals. 2003 Sep-Oct;12(4-5):221-9. doi: 10.1159/000074624. Neurosignals. 2003. PMID: 14673209 Review.
-
The role of CDK5/P25 formation/inhibition in neurodegeneration.Drug News Perspect. 2006 Oct;19(8):453-60. doi: 10.1358/dnp.2006.19.8.1043961. Drug News Perspect. 2006. PMID: 17160145 Review.
Cited by
-
Phytochemicals Targeting Oxidative Stress, Interconnected Neuroinflammatory, and Neuroapoptotic Pathways Following Radiation.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022;20(5):836-856. doi: 10.2174/1570159X19666210809103346. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34370636 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroprotective Effects of Kukoamine a against Radiation-induced Rat Brain Injury through Inhibition of Oxidative Stress and Neuronal Apoptosis.Neurochem Res. 2016 Oct;41(10):2549-2558. doi: 10.1007/s11064-016-1967-0. Epub 2016 May 30. Neurochem Res. 2016. PMID: 27241194
-
Cold Atmospheric Plasma Treatment Induces Anti-Proliferative Effects in Prostate Cancer Cells by Redox and Apoptotic Signaling Pathways.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 1;10(7):e0130350. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130350. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26132846 Free PMC article.
-
CDK5 Regulates Paclitaxel Sensitivity in Ovarian Cancer Cells by Modulating AKT Activation, p21Cip1- and p27Kip1-Mediated G1 Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 6;10(7):e0131833. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0131833. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26146988 Free PMC article.
-
UV irradiation to mouse skin decreases hippocampal neurogenesis and synaptic protein expression via HPA axis activation.Sci Rep. 2017 Nov 14;7(1):15574. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-15773-z. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29138442 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

