Endostatin, an angiogenesis inhibitor, ameliorates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats
- PMID: 23688086
- PMCID: PMC3668162
- DOI: 10.1186/1465-9921-14-56
Endostatin, an angiogenesis inhibitor, ameliorates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats
Abstract
Background: Recent evidence has demonstrated the role of angiogenesis in the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis. Endostatin, a proteolytic fragment of collagen XVIII, is a potent inhibitor of angiogenesis. The aim of our study was to assess whether endostatin has beneficial effects on bleomycin (BLM)-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats.
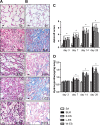
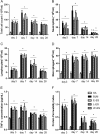
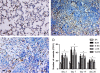
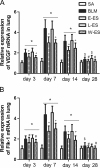
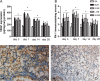
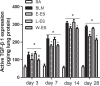
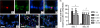
Methods: The rats were randomly divided into five experimental groups: (A) saline only, (B) BLM only, (C) BLM plus early endostatin treatment, (D) BLM plus late endostatin treatment, and (F) BLM plus whole-course endostatin treatment. We investigated the microvascular density (MVD), inflammatory response and alveolar epithelial cell apoptosis in rat lungs in each group at different phases of disease development.
Results: Early endostatin administration attenuated fibrotic changes in BLM-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats. Endostatin treatment decreased MVD by inhibiting the expression of VEGF/VEGFR-2 (Flk-1) and the activation of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2). Endostatin treatment also decreased the number of inflammatory cells infiltrating the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid during the early inflammatory phase of BLM-induced pulmonary fibrosis. In addition, the levels of tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1) were reduced by endostatin treatment. Furthermore, endostatin decreased alveolar type II cell apoptosis and had an epithelium-protective effect. These might be the mechanism underlying the preventive effect of endostatin on pulmonary fibrosis.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that endostatin treatment inhibits the increased MVD, inflammation and alveolar epithelial cell apoptosis, consequently ameliorating BLM-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Effects of andrographolide on the concentration of cytokines in BALF and the expressions of type I and III collagen mRNA in lung tissue in bleomycin-induced rat pulmonary fibrosis].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2011 Jul;27(7):725-9. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 21722520 Chinese.
-
Kallistatin protects against bleomycin-induced idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting angiogenesis and inflammation.Am J Transl Res. 2017 Mar 15;9(3):999-1011. eCollection 2017. Am J Transl Res. 2017. PMID: 28386328 Free PMC article.
-
Tanshinone IIA ameliorates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis and inhibits transforming growth factor-beta-β-dependent epithelial to mesenchymal transition.J Surg Res. 2015 Jul;197(1):167-75. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2015.02.062. Epub 2015 Mar 13. J Surg Res. 2015. PMID: 25911951
-
Role of endostatin in fibroproliferative disorders.-as a candidate for anti-fibrosis therapy-.Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi. 2013;36(6):452-8. doi: 10.2177/jsci.36.452. Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi. 2013. PMID: 24390105 Review.
-
Endostatin in fibrosis and as a potential candidate of anti-fibrotic therapy.Drug Deliv. 2021 Dec;28(1):2051-2061. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2021.1983071. Drug Deliv. 2021. PMID: 34595978 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
NSFC spurs significant basic research progress of respiratory medicine in China.Clin Respir J. 2017 May;11(3):271-284. doi: 10.1111/crj.12351. Epub 2015 Aug 12. Clin Respir J. 2017. PMID: 26176299 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KCa3.1 channel blockade attenuates microvascular remodelling in a large animal model of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 27;9(1):19893. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-56412-z. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31882807 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular matrix dynamics in vascular remodeling.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020 Sep 1;319(3):C481-C499. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00147.2020. Epub 2020 Jun 24. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32579472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The mapping of mRNA alterations elucidates the etiology of radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis.Front Genet. 2022 Oct 24;13:999127. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.999127. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36353104 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular dysfunction in aged mice contributes to persistent lung fibrosis.Aging Cell. 2020 Aug;19(8):e13196. doi: 10.1111/acel.13196. Epub 2020 Jul 21. Aging Cell. 2020. PMID: 32691484 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Thoracic Society. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: diagnosis and treatment. International consensus statement. American Thoracic Society (ATS), and the European Respiratory Society (ERS) Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000;161:646–664. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

