Transient expansion of activated CD8(+) T cells characterizes tuberculosis-associated immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in patients with HIV: a case control study
- PMID: 23688318
- PMCID: PMC3679878
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-9255-10-21
Transient expansion of activated CD8(+) T cells characterizes tuberculosis-associated immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in patients with HIV: a case control study
Abstract
Background: CD4(+) T cell activation indicators have been reported to be a common phenomenon underlying diverse manifestations of immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS). However, we have found that a high frequency of circulating CD8(+) T cells is a specific risk factor for mycobacterial IRIS. Therefore, we investigated whether CD8(+) T cells from patients who develop TB IRIS were specifically activated.
Methods: We obtained PBMCs from HIV+ patients prior to and 4, 8, 12, 24, 52 and 104 weeks after initiating antiretroviral therapy. CD38 and HLADR expression on naive, central memory and effector memory CD8(+) and CD4(+) T cells were determined by flow cytometry. Absolute counts and frequencies of CD8(+) T cell subsets were compared between patients who developed TB IRIS, who developed other IRIS forms and who remained IRIS-free.
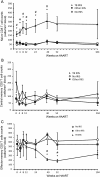
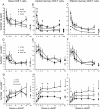
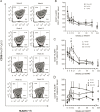
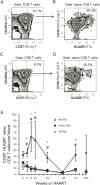
Results: TB IRIS patients showed significantly higher counts of naive CD8(+) T cells than the other groups at most time points, with a contraction of the effector memory subpopulation occurring later in the follow-up period. Activated (CD38(+) HLADR(+)) CD8(+) T cells from all groups decreased with treatment but transiently peaked in TB IRIS patients. This increase was due to an increase in activated naive CD8(+) T cell counts during IRIS. Additionally, the CD8(+) T cell subpopulations of TB IRIS patients expressed HLADR without CD38 more frequently and expressed CD38 without HLADR less frequently than cells from other groups.
Conclusions: CD8(+) T cell activation is specifically relevant to TB IRIS. Different IRIS forms may involve different alterations in T cell subsets, suggesting different underlying inflammatory processes.
Keywords: Activation; CD8 T cells; HIV-1; HIV-2; Highly active anti-retroviral therapy (HAART); Human immunodeficiency virus (AIDS); Inflammation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lower Pre-Treatment T Cell Activation in Early- and Late-Onset Tuberculosis-Associated Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 24;10(7):e0133924. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133924. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26208109 Free PMC article.
-
Frequency of CXCR3+ CD8+ T-Lymphocyte Subsets in Peripheral Blood Is Associated With the Risk of Paradoxical Tuberculosis-Associated Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome Development in Advanced HIV Disease.Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 1;13:873985. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.873985. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35432354 Free PMC article.
-
Robust Reconstitution of Tuberculosis-Specific Polyfunctional CD4+ T-Cell Responses and Rising Systemic Interleukin 6 in Paradoxical Tuberculosis-Associated Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome.Clin Infect Dis. 2016 Mar 15;62(6):795-803. doi: 10.1093/cid/civ978. Epub 2015 Nov 26. Clin Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 26611774 Free PMC article.
-
TB-IRIS, T-cell activation, and remodeling of the T-cell compartment in highly immunosuppressed HIV-infected patients with TB.AIDS. 2015 Jan 28;29(3):263-73. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000000546. AIDS. 2015. PMID: 25486415 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Increased KLRG1 and PD-1 expression on CD8 T lymphocytes in TB-IRIS.PLoS One. 2019 Apr 25;14(4):e0215991. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0215991. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31022273 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Lower Pre-Treatment T Cell Activation in Early- and Late-Onset Tuberculosis-Associated Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 24;10(7):e0133924. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133924. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26208109 Free PMC article.
-
One of the immune activation profiles observed in HIV-1-infected adults with suppressed viremia is linked to metabolic syndrome: The ACTIVIH study.EBioMedicine. 2016 Jun;8:265-276. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.05.008. Epub 2016 May 10. EBioMedicine. 2016. PMID: 27428436 Free PMC article.
-
Frequency of CXCR3+ CD8+ T-Lymphocyte Subsets in Peripheral Blood Is Associated With the Risk of Paradoxical Tuberculosis-Associated Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome Development in Advanced HIV Disease.Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 1;13:873985. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.873985. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35432354 Free PMC article.
-
Differential expression of CXCR3 and CCR6 on CD4+ T-lymphocytes with distinct memory phenotypes characterizes tuberculosis-associated immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome.Sci Rep. 2019 Feb 6;9(1):1502. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-37846-3. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30728405 Free PMC article.
-
CNS immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome.Handb Clin Neurol. 2018;152:167-176. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-63849-6.00013-X. Handb Clin Neurol. 2018. PMID: 29604974 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Oliver BG, Elliott JH, Price P, Phillips M, Saphonn V, Vun MC, Kaldor JM, Cooper DA, French MA. Mediators of innate and adaptive immune responses differentially affect immune restoration disease associated with Mycobacterium tuberculosis in HIV patients beginning antiretroviral therapy. J Infect Dis. 2010;202:1728–1737. doi: 10.1086/657082. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

