Partial venom gland transcriptome of a Drosophila parasitoid wasp, Leptopilina heterotoma, reveals novel and shared bioactive profiles with stinging Hymenoptera
- PMID: 23688557
- PMCID: PMC3905606
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.04.080
Partial venom gland transcriptome of a Drosophila parasitoid wasp, Leptopilina heterotoma, reveals novel and shared bioactive profiles with stinging Hymenoptera
Abstract
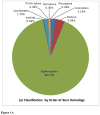
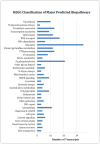
Analysis of natural host-parasite relationships reveals the evolutionary forces that shape the delicate and unique specificity characteristic of such interactions. The accessory long gland-reservoir complex of the wasp Leptopilina heterotoma (Figitidae) produces venom with virus-like particles. Upon delivery, venom components delay host larval development and completely block host immune responses. The host range of this Drosophila endoparasitoid notably includes the highly-studied model organism, Drosophila melanogaster. Categorization of 827 unigenes, using similarity as an indicator of putative homology, reveals that approximately 25% are novel or classified as hypothetical proteins. Most of the remaining unigenes are related to processes involved in signaling, cell cycle, and cell physiology including detoxification, protein biogenesis, and hormone production. Analysis of L. heterotoma's predicted venom gland proteins demonstrates conservation among endo- and ectoparasitoids within the Apocrita (e.g., this wasp and the jewel wasp Nasonia vitripennis) and stinging aculeates (e.g., the honey bee and ants). Enzyme and KEGG pathway profiling predicts that kinases, esterases, and hydrolases may contribute to venom activity in this unique wasp. To our knowledge, this investigation is among the first functional genomic studies for a natural parasitic wasp of Drosophila. Our findings will help explain how L. heterotoma shuts down its hosts' immunity and shed light on the molecular basis of a natural arms race between these insects.
Keywords: A; APIME; Acph/ACPH; Apis mellifera; Asp–Tyr–Asp; C; CBP; CDD; CO(2); CUNY; City University of New York; Conserved Domain Database; DNA; Drosophila; EBI; EC; EST; Enzyme Commission; European Bioinformatics Institute; Expressed Sequence Tags database; FA; Functional genomics; G; GEF; Glu–Cys; IgE; JAK-STAT; JH; Janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription; KAAS; KEGG; KEGG Automatic Annotation Server; Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes; Leptopilina heterotoma; Lh; MAP; MRJP; MUSCLE; Multiple Sequence Comparison by Log-Expectation; N; NCBI; NF-kappa B; NIH; NRI; NSF; National Center for Biotechnology Information; National Institutes of Health; National Research Initiative; National Science Foundation; OBP; ORF; PBP_BOBP; PCR; PDV; PF; PKG; PLB; PRIAM; PSI; PTM; Parasitoid; Pfam accession number; Position-Specific Iterated; Profils pour l'Identification Automatique du Métabolisme; RISE; RNA; RNA Recognition Motif; RRM; Research Initiative for Scientific Enhancement; SMART; STKc-PKA; Ser/Thr; Serine/Threonine Kinase, cAMP-dependent Protein Kinase; Simple Modular Architecture Research Tool; T; TCA; Transcriptome; USDA; United States Department of Agriculture; VLP; Venom gland; acid phosphatase; adenosine; any nucleotide; aspartate–tyrosine–aspartate; base pair; bp; cDNA; cGMP; carbon dioxide; chemosensory-binding protein; complementary deoxyribonucleic acid; cyclic guanosine monophosphate; cyclic guanosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase; cytidine; dbEST; deoxyribonucleic acid; dir; direct; expressed sequence tag; farnesoic acid; for; foraging gene; glutamate–cysteine; guanine nucleotide exchange factor; guanosine; h; hours; immunoglobulin E; juvenile hormone; kD; kiloDalton; major royal jelly protein; mer; microgram; milliliter; mitogen-activated protein; ml; nanogram; ng; non-redundant; nr; nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; odorant-binding protein; open reading frame; pheromone-binding protein/general odorant-binding protein; phospholipase B; poly adenosine monophosphate; polyA; polyDNA virus; polymerase chain reaction; post-translation modification; repeating unit; rev; reverse; ribonucleic acid; serine/threonine; species pluralis; spp.; thymidine; tricarboxylic acid; virus-like particle; w; white; y; yellow; μg.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Integrative approach reveals composition of endoparasitoid wasp venoms.PLoS One. 2013 May 23;8(5):e64125. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064125. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23717546 Free PMC article.
-
Immune Suppressive Extracellular Vesicle Proteins of Leptopilina heterotoma Are Encoded in the Wasp Genome.G3 (Bethesda). 2020 Jan 7;10(1):1-12. doi: 10.1534/g3.119.400349. G3 (Bethesda). 2020. PMID: 31676506 Free PMC article.
-
An introduction to parasitic wasps of Drosophila and the antiparasite immune response.J Vis Exp. 2012 May 7;(63):e3347. doi: 10.3791/3347. J Vis Exp. 2012. PMID: 22588641 Free PMC article.
-
Virulence factors and strategies of Leptopilina spp.: selective responses in Drosophila hosts.Adv Parasitol. 2009;70:123-45. doi: 10.1016/S0065-308X(09)70005-3. Adv Parasitol. 2009. PMID: 19773069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Components of Asobara venoms and their effects on hosts.Adv Parasitol. 2009;70:217-32. doi: 10.1016/S0065-308X(09)70008-9. Adv Parasitol. 2009. PMID: 19773072 Review.
Cited by
-
Whole Transcriptome of the Venom Gland from Urodacus yaschenkoi Scorpion.PLoS One. 2015 May 28;10(5):e0127883. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127883. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26020943 Free PMC article.
-
Insight into the Functional Diversification of Lipases in the Endoparasitoid Pteromalus puparum (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae) by Genome-scale Annotation and Expression Analysis.Insects. 2020 Apr 5;11(4):227. doi: 10.3390/insects11040227. Insects. 2020. PMID: 32260574 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Properties of Venom Peptides and Proteins in Solitary vs. Social Hunting Wasps.Toxins (Basel). 2016 Jan 22;8(2):32. doi: 10.3390/toxins8020032. Toxins (Basel). 2016. PMID: 26805885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An integrated transcriptomic and proteomic approach to identify the main Torymus sinensis venom components.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 3;11(1):5032. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-84385-5. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33658582 Free PMC article.
-
Insights from natural host-parasite interactions: the Drosophila model.Dev Comp Immunol. 2014 Jan;42(1):111-23. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2013.06.001. Epub 2013 Jun 10. Dev Comp Immunol. 2014. PMID: 23764256 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahn JE, Zhu-Salzman K. CmCatD, a cathepsin D-like protease has apotential role in insect defense against a phytocystatin. J Insect Physiol. 2009;55:678–685. - PubMed
-
- Albert S, Klaudiny J. The MRJP/YELLOW protein family of Apis mellifera: Identification of new members in the EST library. J of Insect Physiol. 2004;50:51–59. - PubMed
-
- Allemand R, Lemaitre C, Frey F, Bouletreau M, Vavre F, Norlander G, van Alphen J, Carton Y. Phylogeny of six African Leptopilina species (Hymenoptera: Cynipoidea, Figitidae), parasitoids of Drosophila, with description of three new species. Ann Soc entomol Fr (ns) 2002;38:319–332.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

