Stochastic gene expression in mammals: lessons from olfaction
- PMID: 23689023
- PMCID: PMC3755038
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tcb.2013.04.005
Stochastic gene expression in mammals: lessons from olfaction
Abstract
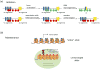
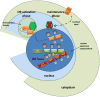
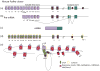
One of the remarkable characteristics of higher organisms is the enormous assortment of cell types that emerge from a common genome. The immune system, with the daunting duty of detecting an astounding number of pathogens, and the nervous system with the equally bewildering task of perceiving and interpreting the external world, are the quintessence of cellular diversity. As we began to appreciate decades ago, achieving distinct expression programs among similar cell types cannot be accomplished solely by deterministic regulatory systems, but by the involvement of some type of stochasticity. In the last few years our understanding of these non-deterministic mechanisms is advancing, and this review will provide a brief summary of the current view of stochastic gene expression with focus on olfactory receptor (OR) gene choice, the epigenetic underpinnings of which recently began to emerge.
Keywords: antigen receptors; clustered protocadherins; epigenetic mechanisms; nuclear architecture; olfactory receptors; stochasticity.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Parallels between Mammalian Mechanisms of Monoallelic Gene Expression.Trends Genet. 2018 Dec;34(12):954-971. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2018.08.005. Epub 2018 Sep 11. Trends Genet. 2018. PMID: 30217559 Review.
-
Opposing, spatially-determined epigenetic forces impose restrictions on stochastic olfactory receptor choice.Elife. 2023 Dec 18;12:RP87445. doi: 10.7554/eLife.87445. Elife. 2023. PMID: 38108811 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin architecture and the generation of antigen receptor diversity.Cell. 2009 Aug 7;138(3):435-48. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.07.016. Cell. 2009. PMID: 19665968 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear architecture and gene silencing in olfactory sensory neurons.Bioarchitecture. 2014;4(4-5):160-3. doi: 10.4161/19490992.2014.982934. Bioarchitecture. 2014. PMID: 25714005 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of odorant receptors: one allele at a time.Hum Mol Genet. 2005 Apr 15;14 Spec No 1:R33-9. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddi105. Hum Mol Genet. 2005. PMID: 15809271 Review.
Cited by
-
Intercellular Variability in Protein Levels from Stochastic Expression and Noisy Cell Cycle Processes.PLoS Comput Biol. 2016 Aug 18;12(8):e1004972. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004972. eCollection 2016 Aug. PLoS Comput Biol. 2016. PMID: 27536771 Free PMC article.
-
A role of stochastic phenotype switching in generating mosaic endothelial cell heterogeneity.Nat Commun. 2016 Jan 8;7:10160. doi: 10.1038/ncomms10160. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 26744078 Free PMC article.
-
Gram-positive bacteria are primed for surviving lethal doses of antibiotics and chemical stress.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 7:2024.05.28.596288. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.28.596288. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Commun Biol. 2025 Feb 08;8(1):206. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-07639-2. PMID: 38895422 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
The HUSH complex controls brain architecture and protocadherin fidelity.Sci Adv. 2022 Nov 4;8(44):eabo7247. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abo7247. Epub 2022 Nov 4. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 36332029 Free PMC article.
-
Rare event of histone demethylation can initiate singular gene expression of olfactory receptors.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Dec 24;110(52):21148-52. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1321511111. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 24344257 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Apostolou E, Thanos D. Virus Infection Induces NF-kappaB-dependent interchromosomal associations mediating monoallelic IFN-beta gene expression. Cell. 2008;134:85–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

