A combined approach of quantitative interaction proteomics and live-cell imaging reveals a regulatory role for endoplasmic reticulum (ER) reticulon homology proteins in peroxisome biogenesis
- PMID: 23689284
- PMCID: PMC3769320
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.M112.017830
A combined approach of quantitative interaction proteomics and live-cell imaging reveals a regulatory role for endoplasmic reticulum (ER) reticulon homology proteins in peroxisome biogenesis
Abstract
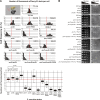
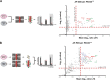
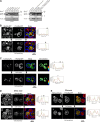
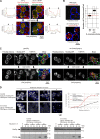
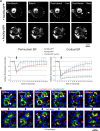
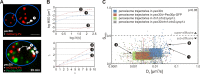
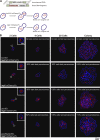
Peroxisome biogenesis initiates at the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and maturation allows for the formation of metabolically active organelles. Yet, peroxisomes can also multiply by growth and division. Several proteins, called peroxins, are known to participate in these processes but little is known about their organization to orchestrate peroxisome proliferation. Here, we demonstrate that regulation of peroxisome proliferation relies on the integrity of the tubular ER network. Using a dual track SILAC-based quantitative interaction proteomics approach, we established a comprehensive network of stable as well as transient interactions of the peroxin Pex30p, an integral membrane protein. Through association with merely ER resident proteins, in particular with proteins containing a reticulon homology domain, and with other peroxins, Pex30p designates peroxisome contact sites at ER subdomains. We show that Pex30p traffics through the ER and segregates in punctae to which peroxisomes specifically append, and we ascertain its transient interaction with all subunits of the COPI coatomer complex suggesting the involvement of a vesicle-mediated transport. We establish that the membrane protein Pex30p facilitates the connection of peroxisomes to the ER. Taken together, our data indicate that Pex30p-containing protein complexes act as focal points from which peroxisomes can form and that the tubular ER architecture organized by the reticulon homology proteins Rtn1p, Rtn2p and Yop1p controls this process.
Figures

References
-
- Wanders R. J., Waterham H. R. (2006) Biochemistry of mammalian peroxisomes revisited. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 75, 295–332 - PubMed
-
- Faust P. L., Kaye E. M., Powers J. M. (2010) Myelin lesions associated with lysosomal and peroxisomal disorders. Expert Rev. Neurother. 10, 1449–1466 - PubMed
-
- Steinberg S. J., Dodt G., Raymond G. V., Braverman N. E., Moser A. B., Moser H. W. (2006) Peroxisome biogenesis disorders. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1763, 1733–1748 - PubMed
-
- Distel B., Erdmann R., Gould S. J., Blobel G., Crane D. I., Cregg J. M., Dodt G., Fujiki Y., Goodman J. M., Just W. W., Kiel J. A., Kunau W. H., Lazarow P. B., Mannaerts G. P., Moser H. W., Osumi T., Rachubinski R. A., Roscher A., Subramani S., Tabak H. F., Tsukamoto T., Valle D., van der Klei I., van Veldhoven P. P., Veenhuis M. (1996) A unified nomenclature for peroxisome biogenesis factors. J. Cell Biol. 135, 1–3 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

