High rate of disease-related copy number variations in childhood onset schizophrenia
- PMID: 23689535
- PMCID: PMC5157161
- DOI: 10.1038/mp.2013.59
High rate of disease-related copy number variations in childhood onset schizophrenia
Abstract
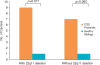
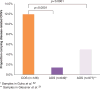
Copy number variants (CNVs) are risk factors in neurodevelopmental disorders, including autism, epilepsy, intellectual disability (ID) and schizophrenia. Childhood onset schizophrenia (COS), defined as onset before the age of 13 years, is a rare and severe form of the disorder, with more striking array of prepsychotic developmental disorders and abnormalities in brain development. Because of the well-known phenotypic variability associated with pathogenic CNVs, we conducted whole genome genotyping to detect CNVs and then focused on a group of 46 rare CNVs that had well-documented risk for adult onset schizophrenia (AOS), autism, epilepsy and/or ID. We evaluated 126 COS probands, 69 of which also had a healthy full sibling. When COS probands were compared with their matched related controls, significantly more affected individuals carried disease-related CNVs (P=0.017). Moreover, COS probands showed a higher rate than that found in AOS probands (P<0.0001). A total of 15 (11.9%) subjects exhibited at least one such CNV and four of these subjects (26.7%) had two. Five of 15 (4.0% of the sample) had a 2.5-3 Mb deletion mapping to 22q11.2, a rate higher than that reported for adult onset (0.3-1%) (P<0.001) or autism spectrum disorder and, indeed, the highest rate reported for any clinical population to date. For one COS subject, a duplication found at 22q13.3 had previously only been associated with autism, and for four patients CNVs at 8q11.2, 10q22.3, 16p11.2 and 17q21.3 had only previously been associated with ID. Taken together, these findings support the well-known pleiotropic effects of these CNVs suggesting shared abnormalities early in brain development. Clinically, broad CNV-based population screening is needed to assess their overall clinical burden.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-IV. 4th. American Psychiatric Association; Washington, DC, USA: 1994. p. 866.
-
- Hall JM, Lee MK, Newman B, Morrow JE, Anderson LA, Huey B, et al. Linkage of early-onset familial breast cancer to chromosome 17q21. Science. 1990;250:1684–1689. - PubMed
-
- Murrell J, Farlow M, Ghetti B, Benson MD. A mutation in the amyloid precursor protein associated with hereditary Alzheimer’s disease. Science. 1991;254:97–99. - PubMed
-
- Walsh T, McClellan JM, McCarthy SE, Addington AM, Pierce SB, Cooper GM, et al. Rare structural variants disrupt multiple genes in neurodevelopmental pathways in schizophrenia. Science. 2008;320:539–543. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous