Transmembrane protein PERP is a component of tessellate junctions and of other junctional and non-junctional plasma membrane regions in diverse epithelial and epithelium-derived cells
- PMID: 23689684
- PMCID: PMC3691483
- DOI: 10.1007/s00441-013-1645-3
Transmembrane protein PERP is a component of tessellate junctions and of other junctional and non-junctional plasma membrane regions in diverse epithelial and epithelium-derived cells
Abstract
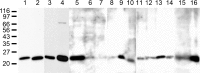
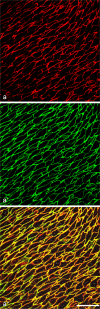
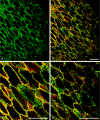
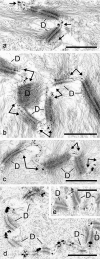
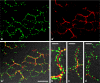
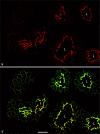
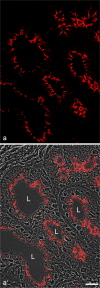
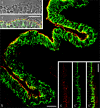
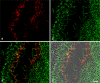
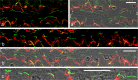
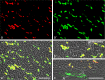
Protein PERP (p53 apoptosis effector related to PMP-22) is a small (21.4 kDa) transmembrane polypeptide with an amino acid sequence indicative of a tetraspanin character. It is enriched in the plasma membrane and apparently contributes to cell-cell contacts. Hitherto, it has been reported to be exclusively a component of desmosomes of some stratified epithelia. However, by using a series of newly generated mono- and polyclonal antibodies, we show that protein PERP is not only present in all kinds of stratified epithelia but also occurs in simple, columnar, complex and transitional epithelia, in various types of squamous metaplasia and epithelium-derived tumors, in diverse epithelium-derived cell cultures and in myocardial tissue. Immunofluorescence and immunoelectron microscopy allow us to localize PERP predominantly in small intradesmosomal locations and in variously sized, junction-like peri- and interdesmosomal regions ("tessellate junctions"), mostly in mosaic or amalgamated combinations with other molecules believed, to date, to be exclusive components of tight and adherens junctions. In the heart, PERP is a major component of the composite junctions of the intercalated disks connecting cardiomyocytes. Finally, protein PERP is a cobblestone-like general component of special plasma membrane regions such as the bile canaliculi of liver and subapical-to-lateral zones of diverse columnar epithelia and upper urothelial cell layers. We discuss possible organizational and architectonic functions of protein PERP and its potential value as an immunohistochemical diagnostic marker.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Striatins as plaque molecules of zonulae adhaerentes in simple epithelia, of tessellate junctions in stratified epithelia, of cardiac composite junctions and of various size classes of lateral adherens junctions in cultures of epithelia- and carcinoma-derived cells.Cell Tissue Res. 2015 Mar;359(3):779-97. doi: 10.1007/s00441-014-2053-z. Epub 2014 Dec 12. Cell Tissue Res. 2015. PMID: 25501894 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of the p53/p63 regulated desmosomal protein Perp promotes tumorigenesis.PLoS Genet. 2010 Oct 21;6(10):e1001168. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001168. PLoS Genet. 2010. PMID: 20975948 Free PMC article.
-
Tight junctions and compositionally related junctional structures in mammalian stratified epithelia and cell cultures derived therefrom.Eur J Cell Biol. 2002 Aug;81(8):419-35. doi: 10.1078/0171-9335-00270. Eur J Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12234014
-
PERP-ing into diverse mechanisms of cancer pathogenesis: Regulation and role of the p53/p63 effector PERP.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2020 Aug;1874(1):188393. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2020.188393. Epub 2020 Jul 15. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32679166 Review.
-
The junctions that don't fit the scheme: special symmetrical cell-cell junctions of their own kind.Cell Tissue Res. 2009 Oct;338(1):1-17. doi: 10.1007/s00441-009-0849-z. Epub 2009 Aug 14. Cell Tissue Res. 2009. PMID: 19680692 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ER stress-linked autophagy stabilizes apoptosis effector PERP and triggers its co-localization with SERCA2b at ER-plasma membrane junctions.Cell Death Discov. 2019 Sep 3;5:132. doi: 10.1038/s41420-019-0212-4. eCollection 2019. Cell Death Discov. 2019. PMID: 31508245 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin and Ethanol Effects in Trembler-J Schwann Cell Culture.Biomolecules. 2022 Mar 29;12(4):515. doi: 10.3390/biom12040515. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35454103 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic enhancer landscapes in human craniofacial development.Nat Commun. 2024 Mar 6;15(1):2030. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46396-4. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38448444 Free PMC article.
-
Striatins as plaque molecules of zonulae adhaerentes in simple epithelia, of tessellate junctions in stratified epithelia, of cardiac composite junctions and of various size classes of lateral adherens junctions in cultures of epithelia- and carcinoma-derived cells.Cell Tissue Res. 2015 Mar;359(3):779-97. doi: 10.1007/s00441-014-2053-z. Epub 2014 Dec 12. Cell Tissue Res. 2015. PMID: 25501894 Free PMC article.
-
A rim-and-spoke hypothesis to explain the biomechanical roles for cytoplasmic intermediate filament networks.J Cell Sci. 2017 Oct 15;130(20):3437-3445. doi: 10.1242/jcs.202168. J Cell Sci. 2017. PMID: 29032358 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barth M, Schumacher H, Kuhn C, Akhyari P, Lichtenberg A, Franke WW. Cordial connections: molecular ensembles and structures of adhering junctions connecting interstitial cells of cardiac valves in situ and in cell culture. Cell Tissue Res. 2009;337:63–77. doi: 10.1007/s00441-009-0806-x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barth M, Rickelt S, Noffz E, Winter-Simanowski S, Niemann H, Akhyari P, Lichtenberg A, Franke WW. The adhering junctions of valvular interstitial cells: molecular composition in fetal and adult hearts and the comings and goings of plakophilin-2 in situ, in cell culture and upon re-association with scaffolds. Cell Tissue Res. 2012;348:295–307. doi: 10.1007/s00441-011-1315-2. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

