Lumpectomy plus tamoxifen with or without irradiation in women age 70 years or older with early breast cancer: long-term follow-up of CALGB 9343
- PMID: 23690420
- PMCID: PMC3691356
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2012.45.2615
Lumpectomy plus tamoxifen with or without irradiation in women age 70 years or older with early breast cancer: long-term follow-up of CALGB 9343
Abstract
Purpose: To determine whether there is a benefit to adjuvant radiation therapy after breast-conserving surgery and tamoxifen in women age ≥ 70 years with early-stage breast cancer.
Patients and methods: Between July 1994 and February 1999, 636 women (age ≥ 70 years) who had clinical stage I (T1N0M0 according to TNM classification) estrogen receptor (ER) -positive breast carcinoma treated by lumpectomy were randomly assigned to receive tamoxifen plus radiation therapy (TamRT; 317 women) or tamoxifen alone (Tam; 319 women). Primary end points were time to local or regional recurrence, frequency of mastectomy, breast cancer-specific survival, time to distant metastasis, and overall survival (OS).
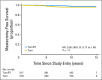
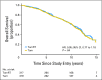
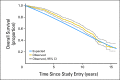
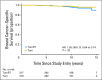
Results: Median follow-up for treated patients is now 12.6 years. At 10 years, 98% of patients receiving TamRT (95% CI, 96% to 99%) compared with 90% of those receiving Tam (95% CI, 85% to 93%) were free from local and regional recurrences. There were no significant differences in time to mastectomy, time to distant metastasis, breast cancer-specific survival, or OS between the two groups. Ten-year OS was 67% (95% CI, 62% to 72%) and 66% (95% CI, 61% to 71%) in the TamRT and Tam groups, respectively.
Conclusion: With long-term follow-up, the previously observed small improvement in locoregional recurrence with the addition of radiation therapy remains. However, this does not translate into an advantage in OS, distant disease-free survival, or breast preservation. Depending on the value placed on local recurrence, Tam remains a reasonable option for women age ≥ 70 years with ER-positive early-stage breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures



Comment in
-
Should a woman age 70 to 80 years receive radiation after breast-conserving surgery?J Clin Oncol. 2013 Jul 1;31(19):2377-81. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.48.3875. Epub 2013 May 20. J Clin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23690415
-
Radiation treatments after breast-conserving therapy for elderly patients.J Clin Oncol. 2013 Jul 1;31(19):2367-8. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.48.0939. Epub 2013 May 20. J Clin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23690425 No abstract available.
-
Reply to P.G. Tsoutsou et al, o. Kaidar-Person et al, and A. Courdi et al.J Clin Oncol. 2013 Dec 20;31(36):4571-3. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2013.52.9438. Epub 2013 Nov 4. J Clin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 24190113 No abstract available.
-
Radiotherapy for elderly patients with breast cancer.J Clin Oncol. 2013 Dec 20;31(36):4571. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2013.52.8943. Epub 2013 Nov 4. J Clin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 24190115 No abstract available.
-
Should radiotherapy be omitted in women age 70 years or older with early breast cancer?J Clin Oncol. 2013 Dec 20;31(36):4569. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2013.51.5312. Epub 2013 Nov 4. J Clin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 24190120 No abstract available.
-
Radiotherapy options after breast-conserving surgery: how can selection of patients be refined?J Clin Oncol. 2013 Dec 20;31(36):4570-1. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2013.52.8299. Epub 2013 Nov 4. J Clin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 24190122 No abstract available.
References
-
- Fisher B, Bryant J, Dignam JJ, et al. Tamoxifen, radiation therapy, or both for prevention of ipsilateral breast tumor recurrence after lumpectomy in women with invasive breast cancers of one centimeter or less. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:4141–4149. - PubMed
-
- Blamey RW, Chetty U, Bates T, et al. Radiotherapy and/or tamoxifen after conserving surgery for breast cancers of excellent prognosis: BASO II trial. Eur J Cancer. 2008;6:55. suppl. - PubMed
-
- Fyles AW, McCready DR, Manchul LA, et al. Tamoxifen with or without breast irradiation in women 50 years or older with early breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:963–970. - PubMed
-
- Pötter R, Gnant M, Kwasny W, et al. Lumpectomy plus tamoxifen or anastrozole with or without whole breast irradiation in women with favorable early breast cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007;68:334–340. - PubMed
-
- Winzer KJ, Sauerbrei W, Braun M, et al. Radiation therapy and tamoxifen after breast-conserving surgery: Updated results of a 2×2 randomised clinical trial in patients with low risk of recurrence. Eur J Cancer. 2010;46:95–101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

