GPR37 and GPR37L1 are receptors for the neuroprotective and glioprotective factors prosaptide and prosaposin
- PMID: 23690594
- PMCID: PMC3677493
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1219004110
GPR37 and GPR37L1 are receptors for the neuroprotective and glioprotective factors prosaptide and prosaposin
Abstract
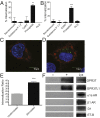
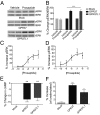
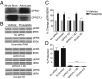
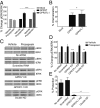
GPR37 (also known as Pael-R) and GPR37L1 are orphan G protein-coupled receptors that are almost exclusively expressed in the nervous system. We screened these receptors for potential activation by various orphan neuropeptides, and these screens yielded a single positive hit: prosaptide, which promoted the endocytosis of GPR37 and GPR37L1, bound to both receptors and activated signaling in a GPR37- and GPR37L1-dependent manner. Prosaptide stimulation of cells transfected with GPR37 or GPR37L1 induced the phosphorylation of ERK in a pertussis toxin-sensitive manner, stimulated (35)S-GTPγS binding, and promoted the inhibition of forskolin-stimulated cAMP production. Because prosaptide is the active fragment of the secreted neuroprotective and glioprotective factor prosaposin (also known as sulfated glycoprotein-1), we purified full-length prosaposin and found that it also stimulated GPR37 and GPR37L1 signaling. Moreover, both prosaptide and prosaposin were found to protect primary astrocytes against oxidative stress, with these protective effects being attenuated by siRNA-mediated knockdown of endogenous astrocytic GPR37 or GPR37L1. These data reveal that GPR37 and GPR37L1 are receptors for the neuroprotective and glioprotective factors prosaptide and prosaposin.
Keywords: GPCR; MAPK; deorphanization; neurodegeneration; peptide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lagerström MC, Schiöth HB. Structural diversity of G protein-coupled receptors and significance for drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008;7(4):339–357. - PubMed
-
- Civelli O, Saito Y, Wang Z, Nothacker HP, Reinscheid RK. Orphan GPCRs and their ligands. Pharmacol Ther. 2006;110(3):525–532. - PubMed
-
- Marazziti D, et al. Cloning of GPR37, a gene located on chromosome 7 encoding a putative G-protein-coupled peptide receptor, from a human frontal brain EST library. Genomics. 1997;45(1):68–77. - PubMed
-
- Zeng Z, Su K, Kyaw H, Li Y. A novel endothelin receptor type-B-like gene enriched in the brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1997;233(2):559–567. - PubMed
-
- Donohue PJ, et al. A human gene encodes a putative G protein-coupled receptor highly expressed in the central nervous system. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1998;54(1):152–160. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

