Anti-CD47 antibody-mediated phagocytosis of cancer by macrophages primes an effective antitumor T-cell response
- PMID: 23690610
- PMCID: PMC3703977
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1305569110
Anti-CD47 antibody-mediated phagocytosis of cancer by macrophages primes an effective antitumor T-cell response
Abstract
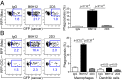
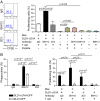
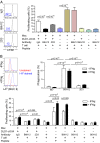
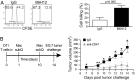
Mobilization of the T-cell response against cancer has the potential to achieve long-lasting cures. However, it is not known how to harness antigen-presenting cells optimally to achieve an effective antitumor T-cell response. In this study, we show that anti-CD47 antibody-mediated phagocytosis of cancer by macrophages can initiate an antitumor T-cell immune response. Using the ovalbumin model antigen system, anti-CD47 antibody-mediated phagocytosis of cancer cells by macrophages resulted in increased priming of OT-I T cells [cluster of differentiation 8-positive (CD8(+))] but decreased priming of OT-II T cells (CD4(+)). The CD4(+) T-cell response was characterized by a reduction in forkhead box P3-positive (Foxp3(+)) regulatory T cells. Macrophages following anti-CD47-mediated phagocytosis primed CD8(+) T cells to exhibit cytotoxic function in vivo. This response protected animals from tumor challenge. We conclude that anti-CD47 antibody treatment not only enables macrophage phagocytosis of cancer but also can initiate an antitumor cytotoxic T-cell immune response.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: I.L.W. owns Amgen Inc. stock and is a Director of Stem Cells, Inc.
Figures


Comment in
-
Perspectives on anti-CD47 antibody treatment for experimental cancer.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Jul 2;110(27):10886-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1308463110. Epub 2013 Jun 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23784781 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

