Fitness costs of synonymous mutations in the rpsT gene can be compensated by restoring mRNA base pairing
- PMID: 23691039
- PMCID: PMC3655191
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063373
Fitness costs of synonymous mutations in the rpsT gene can be compensated by restoring mRNA base pairing
Abstract
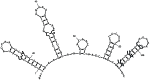
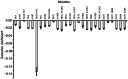
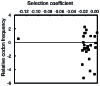
We previously reported that the distribution of fitness effects for non-synonymous and synonymous mutations in Salmonella typhimurium ribosomal proteins S20 and L1 are similar, suggesting that fitness constraints are present at the level of mRNA. Here we explore the hypothesis that synonymous mutations confer their fitness-reducing effect by alterating the secondary structure of the mRNA. To this end, we constructed a set of synonymous substitutions in the rpsT gene, encoding ribosomal protein S20, that are located in predicted paired regions in the mRNA and measured their effect on bacterial fitness. Our results show that for 3/9 cases tested, the reduced fitness conferred by a synonymous mutation could be fully or partly restored by introducing a second synonymous substitution that restore base pairing in a mRNA stem. In addition, random mutations in predicted paired regions had larger fitness effects than those in unpaired regions. Finally, we did not observe any correlation between fitness effects of the synonymous mutations and their rarity. These results suggest that for ribosomal protein S20, the deleterious effects of synonymous mutations are not generally due to codon usage effects, but that mRNA secondary structure is a major fitness constraint.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Eyre-Walker A, Keightley PD (2007) The distribution of fitness effects of new mutations. Nature reviews Genetics 8: 610–618. - PubMed
-
- Jablonka E, Raz G (2009) Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance: prevalence, mechanisms, and implications for the study of heredity and evolution. The Quarterly review of biology 84: 131–176. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

