Nuciferine prevents hepatic steatosis and injury induced by a high-fat diet in hamsters
- PMID: 23691094
- PMCID: PMC3655021
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063770
Nuciferine prevents hepatic steatosis and injury induced by a high-fat diet in hamsters
Abstract
Background: Nuciferine is a major active aporphine alkaloid from the leaves of N. nucifera Gaertn that possesses anti-hyperlipidemia, anti-hypotensive, anti-arrhythmic, and insulin secretagogue activities. However, it is currently unknown whether nuciferine can benefit hepatic lipid metabolism.
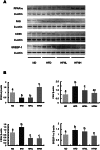
Methodology/principal findings: In the current study, male golden hamsters were randomly divided into four groups fed a normal diet, a high-fat diet (HFD), or a HFD supplemented with nuciferine (10 and 15 mg/kg·BW/day). After 8 weeks of intervention, HFD-induced increases in liver and visceral adipose tissue weight, dyslipidemia, liver steatosis, and mild necroinflammation in hamsters were analyzed. Nuciferine supplementation protected against HFD-induced changes, alleviated necroinflammation, and reversed serum markers of metabolic syndrome in hamsters fed a HFD. RT-PCR and western blot analyses revealed that hamsters fed a HFD had up-regulated levels of genes related to lipogenesis, increased free fatty acid infiltration, and down-regulated genes involved in lipolysis and very low density lipoprotein secretion. In addition, gene expression of cytochrome P4502E1 and tumor necrosis factor-α were also increased in the HFD group. Nuciferine supplementation clearly suppressed HFD-induced alterations in the expression of genes involved in lipid metabolism.
Conclusions/significance: Nuciferine supplementation ameliorated HFD-induced dyslipidemia as well as liver steatosis and injury. The beneficial effects of nuciferine were associated with altered expression of hepatic genes involved in lipid metabolism.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Fan JG, Farrell GC (2009) Epidemiology of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in China. J Hepatol 50: 204–210. - PubMed
-
- Marchesini G, Bugianesi E, Forlani G, Cerrelli F, Lenzi M, et al. (2003) Nonalcoholic fatty liver, steatohepatitis, and the metabolic syndrome. Hepatology 37: 917–923. - PubMed
-
- Luo X, Chen B, Liu J, Yao S (2005) Simultaneous analysis of N-nornuciferine, O-nornuciferine, nuciferine, and roemerine in leaves of Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn by high-performance liquid chromatography–photodiode array detection–electrospray mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 538: 129–133.
-
- Mukherjee PK, Mukherjee D, Maji AK, Rai S, Heinrich M (2009) The sacred lotus (Nelumbo nucifera) - phytochemical and therapeutic profile. J Pharm Pharmacol 61: 407–422. - PubMed
-
- Huang B, Ban X, He J, Tong J, Tian J, et al. (2010) Hepatoprotective and antioxidant activity of ethanolic extracts of edible lotus (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn.) leaves. Food Chemistry 120: 873–878.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

