Toll-like receptor 4 mediates acute lung injury induced by high mobility group box-1
- PMID: 23691208
- PMCID: PMC3656835
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064375
Toll-like receptor 4 mediates acute lung injury induced by high mobility group box-1
Abstract
Background: Acute lung injury (ALI) is considered to be the major cause of respiratory failure in critically ill patients. Clinical studies have found that in patients with sepsis and after hemorrhage, the elevated level of high mobility group box-1(HMGB-1) in their circulation is highly associated with ALI, but the underlying mechanism remains unclear. Extracellular HMGB-1 has cytokine-like properties and can bind to Toll-like Receptor-4 (TLR4), which was reported to play an important role in the pathogenesis of ALI. The aim of this study was to determine whether HMGB-1 directly contributes to ALI and whether TLR4 signaling pathway is involved in this process.
Methods: Recombinant human HMGB-1 (rhHMGB-1) was used to induce ALI in male Sprague-Dawley rats. Lung specimens were collected 2 h after HMGB-1 treatment. The levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, TLR4 protein, and TLR4 mRNA in lungs as well as pathological changes of lung tissue were assessed. In cell studies, the alveolar macrophage cell line, NR8383, was collected 24 h after rhHMGB-1 treatment and the levels of TNF-α and IL-1β in cultured medium as well as TLR4 protein and mRNA levels in the cell were examined. TLR4-shRNA-lentivirus was used to inhibit TLR4 expression, and a neutralizing anti-HMGB1 antibody was used to neutralize rhHMGB-1 both in vitro and in vivo.
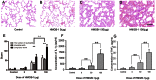
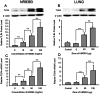
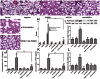
Results: Features of lung injury and significant elevation of IL-1β and TNF-α levels were found in lungs of rhHMGB-1-treated animals. Cultured NR8383 cells were activated by rhHMGB-1 treatment and resulted in the release of IL-1β and TNF-α. TLR4 expression was greatly up-regulated by rhHMGB-1. Inhibition of TLR4 or neutralization of HMGB1 with a specific antibody also attenuated the inflammatory response induced by HMGB-1 both in vivo and in vitro.
Conclusion: HMGB-1 can activate alveolar macrophages to produce proinflammatory cytokines and induce ALI through a mechanism that relies on TLR-4.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
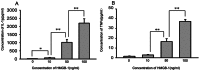
Similar articles
-
Cardiopulmonary Bypass Induces Acute Lung Injury via the High-Mobility Group Box 1/Toll-Like Receptor 4 Pathway.Dis Markers. 2020 Sep 25;2020:8854700. doi: 10.1155/2020/8854700. eCollection 2020. Dis Markers. 2020. PMID: 33062073 Free PMC article.
-
The protective effect of dexmedetomidine on LPS-induced acute lung injury through the HMGB1-mediated TLR4/NF-κB and PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathways.Mol Immunol. 2018 Feb;94:7-17. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2017.12.008. Epub 2017 Dec 11. Mol Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29241031
-
[Effect of qidong huoxue decoction on inflammatory factors and TLR4 mRNA Expression in acute lung injury rats].Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2015 Apr;35(4):438-42. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 26043567 Chinese.
-
High-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) in COVID-19: extrapolation of dangerous liaisons.Inflammopharmacology. 2022 Jun;30(3):811-820. doi: 10.1007/s10787-022-00988-y. Epub 2022 Apr 26. Inflammopharmacology. 2022. PMID: 35471628 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Role of HMGB1 in rheumatic diseases].Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2007 Jul;36(4):412-6. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-9292.2007.04.019. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2007. PMID: 17717837 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
HDAC is essential for epigenetic regulation of Thy-1 gene expression during LPS/TLR4-mediated proliferation of lung fibroblasts.Lab Invest. 2015 Oct;95(10):1105-16. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2015.97. Epub 2015 Jul 27. Lab Invest. 2015. PMID: 26214583
-
Immunomonitoring of Monocyte and Neutrophil Function in Critically Ill Patients: From Sepsis and/or Trauma to COVID-19.J Clin Med. 2021 Dec 12;10(24):5815. doi: 10.3390/jcm10245815. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34945111 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of cisatracurium in combination with ventilation on inflammatory factors and immune variations in sepsis rats.Exp Ther Med. 2018 May;15(5):4414-4418. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.5978. Epub 2018 Mar 20. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 29725382 Free PMC article.
-
Augmenter of liver regeneration (ALR) regulates acute pancreatitis via inhibiting HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway.Am J Transl Res. 2018 Feb 15;10(2):402-410. eCollection 2018. Am J Transl Res. 2018. PMID: 29511434 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiopulmonary Bypass Induces Acute Lung Injury via the High-Mobility Group Box 1/Toll-Like Receptor 4 Pathway.Dis Markers. 2020 Sep 25;2020:8854700. doi: 10.1155/2020/8854700. eCollection 2020. Dis Markers. 2020. PMID: 33062073 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ware LB, Matthay MA (2000) The acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med 342: 1334–1349. - PubMed
-
- Hall RI, Smith MS, Rocker G (1997) The systemic inflammatory response to cardiopulmonary bypass: pathophysiological, therapeutic, and pharmacological considerations. Anesth Analg 85: 766–782. - PubMed
-
- Miller BE, Levy JH (1997) The inflammatory response to cardiopulmonary bypass. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 11: 355–366. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

