Activation of Akt pathway by transcription-independent mechanisms of retinoic acid promotes survival and invasion in lung cancer cells
- PMID: 23693014
- PMCID: PMC3665688
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-12-44
Activation of Akt pathway by transcription-independent mechanisms of retinoic acid promotes survival and invasion in lung cancer cells
Abstract
Background: All-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) is currently being used in clinical trials for cancer treatment. The use of ATRA is limited because some cancers, such as lung cancer, show resistance to treatment. However, little is known about the molecular mechanisms that regulate resistance to ATRA treatment. Akt is a kinase that plays a key role in cell survival and cell invasion. Akt is often activated in lung cancer, suggesting its participation in resistance to chemotherapy. In this study, we explored the hypothesis that activation of the Akt pathway promotes resistance to ATRA treatment at the inhibition of cell survival and invasion in lung cancer. We aimed to provide guidelines for the proper use of ATRA in clinical trials and to elucidate basic biological mechanisms of resistance.
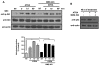
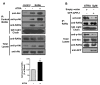
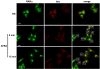
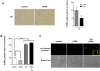
Results: We performed experiments using the A549 human lung adenocarcinoma cell line. We found that ATRA treatment promotes PI3k-Akt pathway activation through transcription-independent mechanisms. Interestingly, ATRA treatment induces the translocation of RARα to the plasma membrane, where it colocalizes with Akt. Immunoprecipitation assays showed that ATRA promotes Akt activation mediated by RARα-Akt interaction. Activation of the PI3k-Akt pathway by ATRA promotes invasion through Rac-GTPase, whereas pretreatment with 15e (PI3k inhibitor) or over-expression of the inactive form of Akt blocks ATRA-induced invasion. We also found that treatment with ATRA induces cell survival, which is inhibited by 15e or over-expression of an inactive form of Akt, through a subsequent increase in the levels of the active form of caspase-3. Finally, we showed that over-expression of the active form of Akt significantly decreases expression levels of the tumor suppressors RARβ2 and p53. In contrast, over-expression of the inactive form of Akt restores RARβ2 expression in cells treated with ATRA, indicating that activation of the PI3k-Akt pathway inhibits the expression of ATRA target genes.
Conclusion: Our results demonstrate that rapid activation of Akt blocks transcription-dependent mechanism of ATRA, promotes invasion and cell survival and confers resistance to retinoic acid treatment in lung cancer cells. These findings provide an incentive for the design and clinical testing of treatment regimens that combine ATRA and PI3k inhibitors for lung cancer treatment.
Figures




Similar articles
-
All-Trans Retinoic Acid Induces Proliferation, Survival, and Migration in A549 Lung Cancer Cells by Activating the ERK Signaling Pathway through a Transcription-Independent Mechanism.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:404368. doi: 10.1155/2015/404368. Epub 2015 Oct 18. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26557664 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Zinc Finger Transcription Factor ZFP580 Facilitates All-Trans Retinoic Acid -Induced Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Differentiation by Rarα-Mediated PI3K/Akt and ERK Signaling.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;50(6):2390-2405. doi: 10.1159/000495098. Epub 2018 Nov 13. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30423583
-
Combination of valproic acid and ATRA restores RARβ2 expression and induces differentiation in cervical cancer through the PI3K/Akt pathway.Curr Mol Med. 2012 Mar;12(3):342-54. doi: 10.2174/156652412799218949. Curr Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22229477
-
Deregulation of All-Trans Retinoic Acid Signaling and Development in Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 28;24(15):12089. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512089. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase signalling pathways in tumor progression, invasion and angiogenesis.Tumori. 2004 Jan-Feb;90(1):2-8. doi: 10.1177/030089160409000102. Tumori. 2004. PMID: 15143962 Review.
Cited by
-
All trans-retinoic acid modulates hyperoxia-induced suppression of NF-kB-dependent Wnt signaling in alveolar A549 epithelial cells.PLoS One. 2022 Aug 10;17(8):e0272769. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0272769. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35947545 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Hyperoxia on Retinoid Metabolism and Retinoid Receptor Expression in the Lungs of Newborn Mice.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 28;10(10):e0140343. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140343. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26509921 Free PMC article.
-
Translation of a Tissue-Selective Rexinoid, UAB30, to the Clinic for Breast Cancer Prevention.Curr Top Med Chem. 2017;17(6):676-695. doi: 10.2174/1568026616666160617093604. Curr Top Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 27320329 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of retinoids in the prevention and treatment of colorectal cancer.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2015 Oct 15;7(10):184-203. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v7.i10.184. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26483874 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current landscape and future directions of therapeutic approaches for adenoid cystic carcinoma of the salivary glands (Review).Oncol Lett. 2025 Jan 22;29(3):153. doi: 10.3892/ol.2025.14899. eCollection 2025 Mar. Oncol Lett. 2025. PMID: 39898287 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hanna N, Shepherd FA, Fossella FV, Pereira JR, De Marinis F, von Pawel J, Gatzemeier U, Tsao TC, Pless M, Muller T, Lim HL, Desch C, Szondy K, Gervais R, Shaharyar Manegold C, Paul S, Paoletti P, Einhorn L, Bunn PA Jr. Randomized phase III trial of pemetrexed versus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer previously treated with chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:1589–1597. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2004.08.163. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

