A long-term, phase 2, multicenter, randomized, open-label, comparative safety study of pomaglumetad methionil (LY2140023 monohydrate) versus atypical antipsychotic standard of care in patients with schizophrenia
- PMID: 23694720
- PMCID: PMC3666887
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-244X-13-143
A long-term, phase 2, multicenter, randomized, open-label, comparative safety study of pomaglumetad methionil (LY2140023 monohydrate) versus atypical antipsychotic standard of care in patients with schizophrenia
Abstract
Background: We compared the time to discontinuation due to lack of tolerability over 24 weeks in patients suffering from schizophrenia treated with pomaglumetad methionil (LY2140023 monohydrate, the prodrug of metabotropic glutamate 2/3 receptor agonist, LY404039) or standard of care (SOC: olanzapine, risperidone, or aripiprazole).
Methods: Study HBBR was a multicenter, randomized, open-label study comparing the long-term safety and tolerability of LY2140023 with SOC for schizophrenia. Patients had moderate symptomatology with prominent negative symptoms and evidence of functional impairment. Those who met entry criteria were randomized to open-label treatment with either LY2140023 (target dose: 40 mg twice daily [BID]; n = 130) or SOC (n = 131).
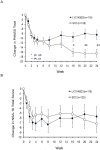
Results: There was no statistically significant difference between LY2140023 and SOC for time to discontinuation due to lack of tolerability (primary objective; P = .184). The Kaplan-Meier estimates revealed comparable time to event profiles. Only 27% of LY2140023 and 45% of SOC patients completed the 24-week open-label, active treatment phase. Twenty-seven patients (20.8%) in the LY2140023 group and 15 patients (11.5%) in the SOC group discontinued due to lack of efficacy (P = .044). Twenty-three patients (17.7%) in the LY2140023 group and 19 patients (14.5%) in the SOC group discontinued due to adverse events (physician and subject decision combined, P = .505). The incidence of serious adverse events was comparable between groups. LY2140023-treated patients reported significantly more treatment-emergent adverse events of vomiting, agitation, and dyspepsia, while SOC-treated patients reported significantly more akathisia and weight gain. The incidence of treatment-emergent parkinsonism (P = .011) and akathisia (P = .029) was significantly greater in SOC group. Improvement in PANSS total score over the initial 6 to 8 weeks of treatment was similar between groups, but improvement was significantly greater in the SOC group at 24-week endpoint (P = .004). LY2140023 and SOC groups had comparable negative symptom improvement at 24-week endpoint (P = .444).
Conclusion: These data provide further evidence that the potential antipsychotic LY2140023 monohydrate, with a glutamatergic mechanism of action, may have a unique tolerability profile characterized by a low association with some adverse events such as extrapyramidal symptoms and weight gain that may characterize currently available dopaminergic antipsychotics.
Trials registration: A Long-term, Phase 2, Multicenter, Randomized, Open-label, Comparative Safety Study of LY2140023 Versus Atypical Antipsychotic Standard of Care in Patients with DSM-IV-TR Schizophrenia.
Figures


References
-
- Rorick-Kehn LM, Johnson BG, Burkey JL, Wright RA, Calligaro DO, Marek GJ, Nisenbaum ES, Catlow JT, Kingston AE, Giera DD, Herin MF, Monn JA, McKinzie DL, Schoepp DD. Pharmacological and pharmacokinetic properties of a structurally novel, potent, and selective metabotropic glutamate 2/3 receptor agonist: in vitro characterization of agonist (−)-(1R,4S,5S,6S)-4-amino-2-sulfonylbicyclo[3.1.0]-hexane-4,6-dicarboxylic acid (LY404039) J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007;321:308–317. doi: 10.1124/jpet.106.110809. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Patil ST, Zhang L, Martenyi F, Lowe SL, Jackson KA, Andreev BV, Avedisova AS, Bardenstein LM, Gurovich IY, Morozova MA, Mosolov SN, Neznanov NG, Reznik AM, Smulevich AB, Tochilov VA, Johnson BG, Monn JA, Schoepp DD. Activation of mGlu2/3 receptors as a new approach to treat schizophrenia: a randomized Phase 2 clinical trial. Nat Med. 2007;13:1102–1107. doi: 10.1038/nm1632. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kinon BJ, Zhang L, Millen BA, Osuntokun OO, Williams JE, Kollack-Walker S, Jackson K, Kryzhanovskaya L, Jarkova N. HBBI Study Group. A multicenter, inpatient, phase 2, double-blind, placebo-controlled dose-ranging study of LY2140023 monohydrate in patients with DSM-IV schizophrenia. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2011;31:349–355. doi: 10.1097/JCP.0b013e318218dcd5. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

