Viral etiologies of infant bronchiolitis, croup and upper respiratory illness during 4 consecutive years
- PMID: 23694832
- PMCID: PMC3880140
- DOI: 10.1097/INF.0b013e31829b7e43
Viral etiologies of infant bronchiolitis, croup and upper respiratory illness during 4 consecutive years
Abstract
Background: Prospective data on viral etiology and clinical characteristics of bronchiolitis and upper respiratory illness (URI) in infants are limited.
Methods: This prospective cohort enrolled previously healthy term infants during inpatient or outpatient visits for acute URI or bronchiolitis during September to May 2004 to 2008. Illness severity was determined using an ordinal bronchiolitis severity score. Common respiratory viruses were identified by real-time reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction.
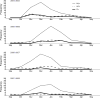
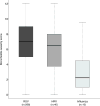
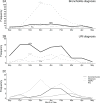
Results: Of 648 infants, 67% were enrolled during inpatient visits and 33% during outpatient visits. Seventy percent had bronchiolitis, 3% croup and 27% URI. Among infants with bronchiolitis, 76% had respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), 18% human rhinovirus (HRV), 10% influenza, 2% coronavirus, 3% human metapneumovirus and 1% parainfluenza virus. Among infants with croup, 39% had HRV, 28% parainfluenza virus, 28% RSV, 11% influenza, 6% coronavirus and none human metapneumovirus. Among infants with URI, 46% had HRV, 14% RSV, 12% influenza, 7% coronavirus, 6% parainfluenza virus and 4% human metapneumovirus. Individual viruses exhibited distinct seasonal, demographic and clinical expression.
Conclusions: The most common infections among infants seeking care in unscheduled medical visits for URI or bronchiolitis were RSV and HRV. Demographic differences were observed between patients with different viruses, suggesting that host and viral factors play a role in phenotypic expression of viral illness.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Shay DK, Holman RC, Newman RD, Liu LL, Stout JW, Anderson LJ. Bronchiolitis-associated hospitalizations among US children, 1980–1996. Jama. 1999;282:1440–6. - PubMed
-
- Singh AM, Moore PE, Gern JE, Lemanske RF, Jr, Hartert TV. Bronchiolitis to asthma: a review and call for studies of gene-virus interactions in asthma causation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;175:108–19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- KL2 RR024977/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K12 ES015855/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- K12 ES 015855/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AI091691-02/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AI 077930/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024975/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI095227/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HS018454/HS/AHRQ HHS/United States
- K24 AI077930/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AI091691/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI 095227/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI085062/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI085062/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HS019669/HS/AHRQ HHS/United States
- KL2 RR24977-03/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AI070808/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

