Microfold (M) cells: important immunosurveillance posts in the intestinal epithelium
- PMID: 23695511
- PMCID: PMC3686595
- DOI: 10.1038/mi.2013.30
Microfold (M) cells: important immunosurveillance posts in the intestinal epithelium
Abstract
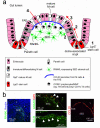
The transcytosis of antigens across the gut epithelium by microfold cells (M cells) is important for the induction of efficient immune responses to some mucosal antigens in Peyer's patches. Recently, substantial progress has been made in our understanding of the factors that influence the development and function of M cells. This review highlights these important advances, with particular emphasis on: the host genes which control the functional maturation of M cells; how this knowledge has led to the rapid advance in our understanding of M-cell biology in the steady state and during aging; molecules expressed on M cells which appear to be used as "immunosurveillance" receptors to sample pathogenic microorganisms in the gut; how certain pathogens appear to exploit M cells to infect the host; and finally how this knowledge has been used to specifically target antigens to M cells to attempt to improve the efficacy of mucosal vaccines.
Figures


References
-
- Lorenz RG, Newberry RD. Isolated lymphoid follicles can function as sites for induction of mucosal immune responses. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 2004;1029:44–57. - PubMed
-
- Tahoun A, et al. Salmonella transforms follicle-associated epithelial cells into M cells to promote intestinal invasion. Cell Host & Microbe. 2012;12:645–666. - PubMed
-
- Mabbott NA, Baillie JC, Hume DA, Freeman TC. Meta-analysis of co-expressed gene signatures in mouse leukocyte populations. Immunobiology. 2010;215:724–736. - PubMed
-
- Bradford BM, Sester D, Hume DA, Mabbott NA. Defining the anatomical localisation of subsets of the murine mononuclear phagocyte system using integrin alpha X (ITGAX) and colony stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1-R) expression fails to discriminate dendritic cells from macrophages. Immunobiology. 2011;216:1228–1237. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BBS/E/D/20251967/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 DK064730/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- BBS/E/D/20251968/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/F019726/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/J0004332/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/J014672/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- JPA1797/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- DK064730/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- BB/K021257/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/G003947/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

