Deletion of a tandem gene family in Arabidopsis: increased MEKK2 abundance triggers autoimmunity when the MEKK1-MKK1/2-MPK4 signaling cascade is disrupted
- PMID: 23695980
- PMCID: PMC3694713
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.113.112102
Deletion of a tandem gene family in Arabidopsis: increased MEKK2 abundance triggers autoimmunity when the MEKK1-MKK1/2-MPK4 signaling cascade is disrupted
Abstract
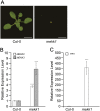
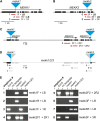
An Arabidopsis thaliana mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase cascade composed of MEKK1, MKK1/MKK2, and MPK4 was previously described as a negative regulator of defense response. MEKK1 encodes a MAP kinase kinase kinase and is a member of a tandemly duplicated gene family with MEKK2 and MEKK3. Using T-DNA insertion lines, we isolated a novel deletion mutant disrupting this gene family and found it to be phenotypically wild-type, in contrast with the mekk1 dwarf phenotype. Follow-up genetic analyses indicated that MEKK2 is required for the mekk1, mkk1 mkk2, and mpk4 autoimmune phenotypes. We next analyzed a T-DNA insertion in the MEKK2 promoter region and found that although it does not reduce the basal expression of MEKK2, it does prevent the upregulation of MEKK2 that is observed in mpk4 plants. This mekk2 allele can rescue the mpk4 autoimmune phenotype in a dosage-dependent manner. We also found that expression of constitutively active MPK4 restored MEKK2 abundance to wild-type levels in mekk1 mutant plants. Finally, using mass spectrometry, we showed that MEKK2 protein levels mirror MEKK2 mRNA levels. Taken together, our results indicate that activated MPK4 is responsible for regulating MEKK2 RNA abundance. In turn, the abundance of MEKK2 appears to be under cellular surveillance such that a modest increase can trigger defense response activation.
Figures








References
-
- Alonso J.M., et al. (2003). Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301: 653–657 - PubMed
-
- Arabidopsis Genome Initiative (2000). Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 408: 796–815 - PubMed
-
- Beck M., Komis G., Ziemann A., Menzel D., Samaj J. (2011). Mitogen-activated protein kinase 4 is involved in the regulation of mitotic and cytokinetic microtubule transitions in Arabidopsis thaliana. New Phytol. 189: 1069–1083 - PubMed
-
- Berriri S., Garcia A.V., Dit Frey N.F., Rozhon W., Pateyron S., Leonhardt N., Montillet J.L., Leung J., Hirt H., Colcombet J. (2012). Constitutively active mitogen-activated protein kinase versions reveal functions of Arabidopsis MPK4 in pathogen defense signaling. Plant Cell 24: 4281–4293 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

