Metastatic non-clear cell renal cell carcinoma treated with targeted therapy agents: characterization of survival outcome and application of the International mRCC Database Consortium criteria
- PMID: 23696129
- PMCID: PMC3934562
- DOI: 10.1002/cncr.28151
Metastatic non-clear cell renal cell carcinoma treated with targeted therapy agents: characterization of survival outcome and application of the International mRCC Database Consortium criteria
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to apply the International mRCC Database Consortium (IMDC) prognostic model in metastatic non-clear cell renal cell carcinoma (nccRCC). In addition, the survival outcome of metastatic nccRCC patients was characterized.
Methods: Data on 2215 patients (1963 with clear-cell RCC [ccRCC] and 252 with nccRCC) treated with first-line VEGF- and mTOR-targeted therapies were collected from the IMDC. Time to treatment failure (TTF) and overall survival (OS) were compared in groups with favorable, intermediate, and poor prognoses according to IMDC prognostic criteria
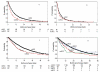
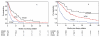
Results: The median OS of the entire cohort was 20.9 months. nccRCC patients were younger (P < .0001) and more often presented with low hemoglobin (P = .014) and elevated neutrophils (P = .0001), but otherwise had clinicopathological features similar to those of ccRCC patients. OS (12.8 vs 22.3 months; P < .0001) and TTF (4.2 vs 7.8 months; P < .0001) were worse in nccRCC patients compared with ccRCC patients. The hazard ratio for death and TTF when adjusted for the prognostic factors was 1.41 (95% CI, 1.19-1.67; P < .0001) and 1.54 (95% CI, 1.33-1.79; P < .0001), respectively. The IMDC prognostic model reliably discriminated 3 risk groups to predict OS and TTF in nccRCC; the median OS of the favorable, intermediate, and poor prognosis groups was 31.4, 16.1, and 5.1 months, respectively (P < .0001), and the median TTF was 9.6, 4.9, and 2.1 months, respectively (P < .0001).
Conclusions: Although targeted agents have significantly improved the outcome of patients with nccRCC, for the majority survival is still inferior compared with patients with ccRCC. The IMDC prognostic model reliably predicts OS and TTF in nccRCC and ccRCC patients.
Keywords: Heng risk criteria; IMDC risk model; non-clear cell renal cell carcinoma; overall survival; prognostication; targeted therapies.
Copyright © 2013 American Cancer Society.
References
-
- Rini BI, Campbell SC, Escudier B. Renal cell carcinoma. Lancet. 2009;373:1119–1132. - PubMed
-
- Lopez-Beltran A, Scarpelli M, Montironi R, Kirkali Z. 2004 WHO classification of the renal tumors of the adults. Eur Urol. 2006;49:798–805. - PubMed
-
- Patard JJ, Pignot G, Escudier B, et al. ICUD-EAU International Consultation on Kidney Cancer 2010: treatment of metastatic disease. Eur Urol. 2011;60:684–690. - PubMed
-
- Escudier B, Eisen T, Stadler WM, et al. Sorafenib in advanced clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:125–134. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous