The secretory pathway calcium ATPase PMR-1/SPCA1 has essential roles in cell migration during Caenorhabditis elegans embryonic development
- PMID: 23696750
- PMCID: PMC3656159
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003506
The secretory pathway calcium ATPase PMR-1/SPCA1 has essential roles in cell migration during Caenorhabditis elegans embryonic development
Abstract
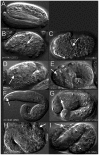
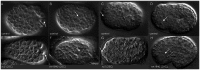
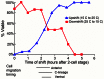
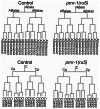
Maintaining levels of calcium in the cytosol is important for many cellular events, including cell migration, where localized regions of high calcium are required to regulate cytoskeletal dynamics, contractility, and adhesion. Studies show inositol-trisphosphate receptors (IP3R) and ryanodine receptors (RyR), which release calcium into the cytosol, are important regulators of cell migration. Similarly, proteins that return calcium to secretory stores are likely to be important for cell migration. The secretory protein calcium ATPase (SPCA) is a Golgi-localized protein that transports calcium from the cytosol into secretory stores. SPCA has established roles in protein processing, metal homeostasis, and inositol-trisphosphate signaling. Defects in the human SPCA1/ATP2C1 gene cause Hailey-Hailey disease (MIM# 169600), a genodermatosis characterized by cutaneous blisters and fissures as well as keratinocyte cell adhesion defects. We have determined that PMR-1, the Caenorhabditis elegans ortholog of SPCA1, plays an essential role in embryogenesis. Pmr-1 strains isolated from genetic screens show terminal phenotypes, such as ventral and anterior enclosure failures, body morphogenesis defects, and an unattached pharynx, which are caused by earlier defects during gastrulation. In Pmr-1 embryos, migration rates are significantly reduced for cells moving along the embryo surface, such as ventral neuroblasts, C-derived, and anterior-most blastomeres. Gene interaction experiments show changing the activity of itr-1/IP3R and unc-68/RyR modulates levels of embryonic lethality in Pmr-1 strains, indicating pmr-1 acts with these calcium channels to regulate cell migration. This analysis reveals novel genes involved in C. elegans cell migration, as well as a new role in cell migration for the highly conserved SPCA gene family.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Brini M, Carafoli E (2009) Calcium pumps in health and disease. Phys Rev 89: 1341–1378. - PubMed
-
- Brundage RA, Fogarty KE, Tuft RA, Fay FS (1991) Calcium gradients underlying polarization and chemotaxis of eosinophils. Science 254: 703–706. - PubMed
-
- Ridley AJ, Schwartz MA, Burridge K, Firtel RA, Ginsberg MH, et al. (2003) Cell Migration: Integrating signals from front to back. Science 302: 1704–1709. - PubMed
-
- Wei C, Wang X, Zheng M, Cheng H (2012) Calcium gradients underlying cell migration. Curr Opin Cell Biol 24: 254–261. - PubMed
-
- Wei C, Wang X, Chen M, Ouyang K, Zheng M, et al. (2010) Flickering calcium microdomains signal turning of migrating cells. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 88: 105–110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

