Complete protein characterization using top-down mass spectrometry and ultraviolet photodissociation
- PMID: 23697802
- PMCID: PMC3757099
- DOI: 10.1021/ja4029654
Complete protein characterization using top-down mass spectrometry and ultraviolet photodissociation
Abstract
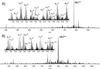
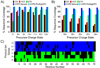
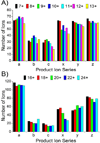
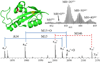
The top-down approach to proteomics offers compelling advantages due to the potential to provide complete characterization of protein sequence and post-translational modifications. Here we describe the implementation of 193 nm ultraviolet photodissociation (UVPD) in an Orbitrap mass spectrometer for characterization of intact proteins. Near-complete fragmentation of proteins up to 29 kDa is achieved with UVPD including the unambiguous localization of a single residue mutation and several protein modifications on Pin1 (Q13526), a protein implicated in the development of Alzheimer's disease and in cancer pathogenesis. The 5 ns, high-energy activation afforded by UVPD exhibits far less precursor ion-charge state dependence than conventional collision- and electron-based dissociation methods.
Figures
References
-
- Duncan MW, Aebersold R, Caprioli RM. Nat Biotech. 2010;28:659–664. - PubMed
-
- Kelleher NL, Lin HY, Valaskovic GA, Aaserud DJ, Fridriksson EK, McLafferty FW. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999;121:806–812.
-
- McLafferty FW, Breuker K, Jin Mi, Han Xuemei, Infusini G, Jiang Honghai, Kong Xianglei, Begley TP. FEBS Journal. 2007;274:6256–6268. - PubMed
-
- Zhou H, Ning Z, E. Starr A, Abu-Farha M, Figeys D. Anal. Chem. 2011;84:720–734. - PubMed
-
- Little DP, Speir JP, Senko MW, O’Connor PB, McLafferty FW. Anal. Chem. 1994;66:2809–2815. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

