Endothelin-1 inhibits sodium reabsorption by ET(A) and ET(B) receptors in the mouse cortical collecting duct
- PMID: 23698114
- PMCID: PMC3891265
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00613.2012
Endothelin-1 inhibits sodium reabsorption by ET(A) and ET(B) receptors in the mouse cortical collecting duct
Abstract
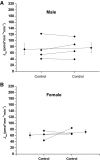
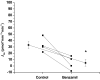
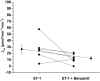
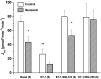
The collecting duct (CD) is a major renal site for the hormonal regulation of Na homeostasis and is critical for systemic arterial blood pressure control. Our previous studies demonstrated that the endothelin-1 gene (edn1) is an early response gene to the action of aldosterone. Because aldosterone and endothelin-1 (ET-1) have opposing actions on Na reabsorption (JNa) in the kidney, we postulated that stimulation of ET-1 by aldosterone acts as a negative feedback mechanism, acting locally within the CD. Aldosterone is known to increase JNa in the CD, in part, by stimulating the epithelial Na channel (ENaC). In contrast, ET-1 increases Na and water excretion through its binding to receptors in the CD. To date, direct measurement of the quantitative effect of ET-1 on transepithelial JNa in the isolated in vitro microperfused mouse CD has not been determined. We observed that the CD exhibits substantial JNa in male and female mice that is regulated, in part, by a benzamil-sensitive pathway, presumably ENaC. ENaC-mediated JNa is greater in the cortical CD (CCD) than in the outer medullary CD (OMCD); however, benzamil-insensitive JNa is present in the CCD and not in the OMCD. In the presence of ET-1, ENaC-mediated JNa is significantly inhibited. Blockade of either ETA or ETB receptor restored JNa to control rates; however, only ETA receptor blockade restored a benzamil-sensitive component of JNa. We conclude 1) Na reabsorption is mediated by ENaC in the CCD and OMCD and also by an ENaC-independent mechanism in the CCD; and 2) ET-1 inhibits JNa in the CCD through both ETA and ETB receptor-mediated pathways.
Keywords: aldosterone; collecting duct; endothelin-1; kidney; mineralocorticoid; sodium reabsorption.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Collecting duct-specific endothelin B receptor knockout increases ENaC activity.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2012 Jan 1;302(1):C188-94. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00301.2011. Epub 2011 Sep 14. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2012. PMID: 21918182 Free PMC article.
-
NOS1-dependent negative feedback regulation of the epithelial sodium channel in the collecting duct.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2015 Feb 1;308(3):F244-51. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00596.2013. Epub 2014 Nov 12. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25391901 Free PMC article.
-
Na delivery and ENaC mediate flow regulation of collecting duct endothelin-1 production.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012 May 15;302(10):F1325-30. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00034.2012. Epub 2012 Feb 22. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22357920 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelin and collecting duct sodium and water transport.Contrib Nephrol. 2011;172:94-106. doi: 10.1159/000328687. Epub 2011 Aug 30. Contrib Nephrol. 2011. PMID: 21893992 Review.
-
Nitric oxide and the A and B of endothelin of sodium homeostasis.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2013 Jan;22(1):26-31. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0b013e32835b4edc. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2013. PMID: 23160444 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Thick Ascending Limb Sodium Transport in the Pathogenesis of Hypertension.Physiol Rev. 2019 Jan 1;99(1):235-309. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00055.2017. Physiol Rev. 2019. PMID: 30354966 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Per1 and the mineralocorticoid receptor in the coordinate regulation of αENaC in renal cortical collecting duct cells.Front Physiol. 2013 Sep 17;4:253. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2013.00253. eCollection 2013. Front Physiol. 2013. PMID: 24062694 Free PMC article.
-
High dietary sodium causes dyssynchrony of the renal molecular clock in rats.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018 Jan 1;314(1):F89-F98. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00028.2017. Epub 2017 Sep 27. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018. PMID: 28971988 Free PMC article.
-
Kidney omics in hypertension: from statistical associations to biological mechanisms and clinical applications.Kidney Int. 2022 Sep;102(3):492-505. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2022.04.045. Epub 2022 Jun 9. Kidney Int. 2022. PMID: 35690124 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Circadian Clock in the Regulation of Renal Rhythms.J Biol Rhythms. 2015 Dec;30(6):470-86. doi: 10.1177/0748730415610879. Epub 2015 Nov 2. J Biol Rhythms. 2015. PMID: 26527094 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Boesen EI. Endothelin ETB receptor heterodimerization: beyond the ETA receptor. Kidney Int 74: 693–694, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Burg MB, Grantham JJ, Abramow M, Orloff J. Preparation and study of fragments of single rabbit nephrons. Am J Physiol 210: 1293–1298, 1966 - PubMed
-
- Chang CT, Sun CY, Pong CY, Chen YC, Lin GP, Chang TC, Wu MS. Interaction of estrogen and progesterone in the regulation of sodium channels in collecting tubular cells. Chang Gung Med J 30: 305–312, 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

