Identification by 16S rRNA gene sequencing of an Actinomyces hongkongensis isolate recovered from a patient with pelvic actinomycosis
- PMID: 23698532
- PMCID: PMC3719606
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00509-13
Identification by 16S rRNA gene sequencing of an Actinomyces hongkongensis isolate recovered from a patient with pelvic actinomycosis
Abstract
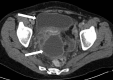
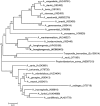
A case of Actinomyces hongkongensis pelvic actinomycosis in an adult woman is described. Conventional phenotypic tests failed to identify the Gram-positive bacillus isolated from a fluid aspirate of a pelvic abscess. The bacterium was identified by 16S rRNA gene sequencing and analysis using the SmartGene Integrated Database Network System software.
Figures
References
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute 2008. Interpretive criteria for identification of bacteria and fungi by DNA target sequencing. Approved standard MM18-A. CLSI, Wayne, PA
-
- Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S. 2007. MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 24:1596–1599 - PubMed
-
- Woo PC, Lau SK, Teng JL, Tse H, Yuen KY. 2008. Then and now: use of 16S rDNA gene sequencing for bacterial identification and discovery of novel bacteria in clinical microbiology laboratories. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 14:908–934 - PubMed
-
- Woo PC, Fung AM, Lau SK, Teng JL, Wong BH, Wong MK, Hon E, Tang GW, Yuen KY. 2003. Actinomyces hongkongensis sp. nov. a novel Actinomyces species isolated from a patient with pelvic actinomycosis. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 26:518–522 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

