TETonic shift: biological roles of TET proteins in DNA demethylation and transcription
- PMID: 23698584
- PMCID: PMC3804139
- DOI: 10.1038/nrm3589
TETonic shift: biological roles of TET proteins in DNA demethylation and transcription
Abstract
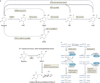
In many organisms, the methylation of cytosine in DNA has a key role in silencing 'parasitic' DNA elements, regulating transcription and establishing cellular identity. The recent discovery that ten-eleven translocation (TET) proteins are 5-methylcytosine oxidases has provided several chemically plausible pathways for the reversal of DNA methylation, thus triggering a paradigm shift in our understanding of how changes in DNA methylation are coupled to cell differentiation, embryonic development and cancer.
Figures

References
-
-
Tahiliani M, et al. Conversion of 5-methylcytosine to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in mammalian DNA by MLL partner TET 1. Science. 2009;324:930–935.Discovery that TET proteins oxidize 5mC to 5hmC
-
-
-
Iyer LM, Tahiliani M, Rao A, Aravind L. Prediction of novel families of enzymes involved in oxidative and other complex modifications of bases in nucleic acids. Cell Cycle. 2009;8:1698–1710.Describes the evolution of TET proteins and the presence of TET homologues in non-metazoan species
-
-
- Ono R, et al. LCX, leukemia-associated protein with a CXXC domain, is fused to MLL in acute myeloid leukemia with trilineage dysplasia having t( 10; 11] (q22;q23) Cancer Res. 2002;62:4075–4080. - PubMed
-
- Lorsbach RB, et al. TET1, pa member of a novel protein family, is fused to MLL in acute myeloid leukemia containing the t(10; 11)(q22;q23) Leukemia. 2003;17:637–641. - PubMed
-
-
Ito S, et al. Tet proteins can convert 5-methylcytosine to 5-formylcytosine and 5-carboxylcytosine. Science. 2011;333:1300–1303.Shows that TET proteins can produce 5fC and 5caC and quantifies the level of modified cytosines in a range of cell types
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

