Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium guidelines for CYP2C19 genotype and clopidogrel therapy: 2013 update
- PMID: 23698643
- PMCID: PMC3748366
- DOI: 10.1038/clpt.2013.105
Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium guidelines for CYP2C19 genotype and clopidogrel therapy: 2013 update
Abstract
Cytochrome P450 (CYP)2C19 catalyzes the bioactivation of the antiplatelet prodrug clopidogrel, and CYP2C19 loss-of-function alleles impair formation of active metabolites, resulting in reduced platelet inhibition. In addition, CYP2C19 loss-of-function alleles confer increased risks for serious adverse cardiovascular (CV) events among clopidogrel-treated patients with acute coronary syndromes (ACSs) undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). Guideline updates include emphasis on appropriate indication for CYP2C19 genotype-directed antiplatelet therapy, refined recommendations for specific CYP2C19 alleles, and additional evidence from an expanded literature review (updates at http://www.pharmgkb.org).
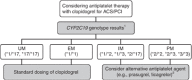
Figures
References
-
- Bouman H.J., et al. Paraoxonase-1 is a major determinant of clopidogrel efficacy. Nat. Med. 2011;17:110–116. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 HL105198/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R24 GM061374/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 GM074492/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U19 HL065962/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR000069/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01HL105198/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL065962/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01GM92666/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- KL2TR000069/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 GM092666/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U19HL065962-10/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01GM074492/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01HL65962/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R24GM61374/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

