The microbiology of malting and brewing
- PMID: 23699253
- PMCID: PMC3668669
- DOI: 10.1128/MMBR.00060-12
The microbiology of malting and brewing
Abstract
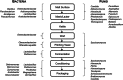
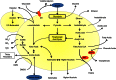
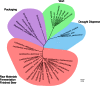
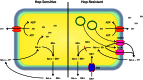
Brewing beer involves microbial activity at every stage, from raw material production and malting to stability in the package. Most of these activities are desirable, as beer is the result of a traditional food fermentation, but others represent threats to the quality of the final product and must be controlled actively through careful management, the daily task of maltsters and brewers globally. This review collates current knowledge relevant to the biology of brewing yeast, fermentation management, and the microbial ecology of beer and brewing.
Figures


References
-
- Bamforth CW. (ed). 2006. Scientific principles of malting and brewing. American Society of Brewing Chemists, St. Paul, MN
-
- Boulton C, Quain DE. (ed). 2001. Brewing yeast and fermentation. Blackwell, Oxford, United Kingdom
-
- Boulton C. 2006. Fermentation of beer, p 228–253 In Bamforth CW. (ed), Brewing: new technologies. Woodhead Publishing, Cambridge, United Kingdom
-
- Barnett JA. 1992. The taxonomy of the genus Saccharomyces Meyen ex Reess—a short review for non-taxonomists. Yeast 8:1–23
-
- Vaughan-Martini A, Martini A. 1998. Saccharomyces Meyen ex Rees, p 358–371 In Kurtzman C, Fell J. (ed), The yeasts: a taxonomic study. Elsevier, Amsterdam, Netherlands
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

